What is call ratio in spread option strategy?
Call ratio is the ratio of leg 1(lower strike) quantity and leg 2(higher strike) quantity. So, Call Ratio= Leg 1 Quantity/Leg 2 Quantity. Ensure that call ratio should be less than 0.67. Leg 2 quantity= 2*leg 1 quantity, or leg2 quantity= 1.5*leg 1 quantity.
Generally, in spread option strategy, the positional quantity of leg 1 and leg 2 is equal whether it is bull call spread option strategy or bear call spread option strategy, but in call ratio spread option strategy, the quantity of leg 1 will be half of the quantity of leg 2 or Will be two thirds. Similarly, in call ratio back spread, the quantity of leg 1 and leg 2 also have the same ratio like call ratio spread option strategy but the buying and selling positions are opposite.
Table of Contents
Call ratio spread option strategy:
The Call Ratio Spread option strategy is applicable when participants (traders/investors) place limits on an underlying asset price which means to be sideways on the underlying asset price (stock or index). It means to say that the spot price will neither rise much nor fall much within the time frame (expiry time). When you implement the call ratio spread option strategy, you get limited profit within the range and unlimited loss if the market moves above the range and limited loss if the market (spot price) moves below the range.
Strategy notes for a call ratio spread option strategy:
The call ratio spread option strategy is a 2 leg option strategy with different quantity as it involves buying one or two ATM (lower strike) call options and selling two or three OTM (higher strike) call options.
To implement call ratio spread-
Leg 1- Buy 1-ATM (LK-lower strike) call option
Leg 2- Sell 2-OTM (HK-higher strike) call option
Or
Leg 1- Buy 2-ATM (LK-lower strike) call option
Leg 2- Sell 3-OTM (HK-higher strike) call option
When take positions ensure that both leg option contracts should be same underlying asset, same expiry date, and with different quantity of options. Also ensure that when you take position in both leg then take position in both leg same time.
Example of call ratio spread option strategy:
For a example of call ratio spread option strategy, we are taking Nifty options contract.
Option contract- Nifty 27Apr … CE
Today’s date- 13/04/2023
Expiry date- 27/04/2023
Expiry days= expiry date – todays date= 14days
Underlying asset- Nifty 50
Directional view/outlook- Sideways
Spot price (S)- 17742/-
Annual historical volatility- 20%
Upper range (2SD)= 17742+2*17742*(20/100)*√(14/365)= 19131.88/-
Spread and strike price selection for a call ratio spread option strategy:
In the table below, we will look at different spreads and different strike combinations to see which one is better. And also we will compare with call ratio of 0.5 and 0.667.
For spread= 100, and call ratio= 0.5,
| Generalization | 1-OTM+2-OTM | 1-ATM+2-OTM | 1-ITM+2-OTM | 1-ITM+2-ATM |
| 1-LK | 17850 | 17750 | 17700 | 17650 |
| 2-HK | 17950 | 17850 | 17800 | 17750 |
| Spread | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| LK-PP | 114.05 | 167.85 | 198.05 | 230.95 |
| HK-PR | 72 | 114.05 | 138.95 | 167.85 |
| Net debit/credit (-PP+2*PR) | +29.95 | +60.25 | +79.85 | +104.75 |
| Max loss (at upper range=19131.89) | -1051.94 (unlimited) | -1121.64 (unlimited) | -1152.04 (unlimited) | -1177.14 (unlimited) |
| Max profit | 129.95 | 160.25 | 179.85 | 204.75 |
| Lower break even point | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Upper break even point | 18079.95 | 18010.25 | 17979.85 | 17954.75 |
| Risk/reward ratio | 8.1 | 7 | 6.41 | 5.8 |
| Remarks | risk reward ratio is very high | looks like moderate | break even point is very close to spot price | break even point is very close to spot price |
According to above table, best combination is 1-ATM+2-OTM.
For spread= 100, and call ratio= 0.667,
| Generalization | 2-OTM+3-OTM | 2-ATM+3-OTM | 2-ITM+3-OTM | 2-ITM+3-ATM |
| 2-LK | 17850 | 17750 | 17700 | 17650 |
| 3-HK | 17950 | 17850 | 17800 | 17750 |
| Spread | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| LK-PP | 114.05 | 167.85 | 198.05 | 230.95 |
| HK-PR | 72 | 114.05 | 138.95 | 167.85 |
| Net debit/credit (-2*PP+3*PR) | -12.10 | +6.45 | +20.75 | +41.65 |
| Max loss (at upper range=19131.89) | -993.99 (unlimited) | -1075.44 (unlimited) | -1111.14 (unlimited) | -1140.24 (unlimited) |
| Max profit | 187.9 | 206.45 | 220.75 | 241.65 |
| Lower break even point | 17856.05 | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Upper break even point | 18137.9 | 18056.45 | 18020.75 | 17991.65 |
| Risk/reward ratio | 5.3 | 5.21 | 5.03 | 4.72 |
| Remarks | risk reward ratio is very high | looks like moderate | break even point is very close to spot price | break even point is very close to spot price |
According to above table, best combination is 2-ATM+3-OTM,
And the best call ratio is 0.667, because of upper break even point is higher than upper break even point of call ratio 0.5, but the net credit is less. So if the spot price is going to fall in the time frame, then take a strike combination with a call ratio of 0.5.
For spread= 200, and call ratio= 0.5,
| Generalization | 1-OTM+2-OTM | 1-ATM+2-OTM | 1-ITM+2-OTM | 1-ITM+2-ATM |
| 1-LK | 17850 | 17750 | 17650 | 17550 |
| 2-HK | 18050 | 17950 | 17850 | 17750 |
| Spread | 200 | 200 | 200 | 200 |
| LK-PP | 114.05 | 167.85 | 230.95 | 306.25 |
| HK-PR | 42.85 | 72.0 | 114.05 | 167.85 |
| Net debit/credit (-PP+2*PR) | -28.35 | -23.85 | -2.85 | +29.45 |
| Max loss (at upper range=19131.89) | -910.24 (unlimited) | -1005.74 (unlimited) | -1084.74 (unlimited) | -1152.44 (unlimited) |
| Max profit | 171.65 | 176.15 | 197.15 | 229.45 |
| Lower break even point | 17878.35 | 17773.85 | 17652.85 | N/A |
| Upper break even point | 18221.65 | 18126.15 | 18047.15 | 17979.45 |
| Risk/reward ratio | 5.3 | 5.71 | 5.5 | 5.02 |
| Remarks | looks like moderate | risk reward ratio is very high | break even point is very close to spot price | break even point is very close to spot price |
According to above table, best combination is 1-slightly OTM+2-OTM.
For spread= 200, and call ratio= 0.667,
| Generalization | 2-OTM+3-OTM | 2-ATM+3-OTM | 2-ITM+3-OTM | 2-ITM+3-ATM |
| 2-LK | 17850 | 17750 | 17650 | 17550 |
| 3-HK | 18050 | 17950 | 17850 | 17750 |
| Spread | 200 | 200 | 200 | 200 |
| LK-PP | 114.05 | 167.85 | 230.95 | 306.25 |
| HK-PR | 42.85 | 72 | 114.05 | 167.85 |
| Net debit/credit (-2*PP+3*PR) | -99.55 | -119.7 | -119.75 | -108.95 |
| Max loss (at upper range=19131.89) | -781.44 (unlimited) | -901.59 (unlimited) | -1001.64 (unlimited) | -1090.84 (unlimited) |
| Max profit | 300.45 | 280.3 | 280.25 | 291.05 |
| Lower break even point | 17899.775 | 17809.85 | 17709.875 | 17604.475 |
| Upper break even point | 18350.45 | 18230.3 | 18130.25 | 18041.05 |
| Risk/reward ratio | 2.6 | 3.22 | 3.57 | 3.75 |
| Remarks | looks like moderate | looks like moderate | break even point is very close to spot price | break even point is very close to spot price |
According to above table, best combination is 1-slightly OTM+2-OTM,
And the best call ratio is 0.667, because of upper break even point is higher than upper break even point of call ratio 0.5, but the net debit is less. So if the spot price is going to fall in the time frame, then take a strike combination with a call ratio of 0.5.
For spread= 300, and call ratio= 0.5,
| Generalization | 1-OTM+2-OTM | 1-ATM+2-OTM | 1-ITM+2-OTM | 1-ITM+2-ATM |
| 1-LK | 17850 | 17750 | 17600 | 17450 |
| 2-HK | 18150 | 18050 | 17900 | 17750 |
| Spread | 300 | 300 | 300 | 300 |
| LK-PP | 114.05 | 167.85 | 268.20 | 386.19 |
| HK-PR | 24.60 | 42.85 | 91.60 | 167.85 |
| Net debit/credit (-PP+2*PR) | -64.85 | -82.15 | -85.00 | -50.49 |
| Max loss (at upper range=19131.89) | -746.74 (unlimited) | -864.04 (unlimited) | -1016.89 (unlimited) | -1132.38 (unlimited) |
| Max profit | 235.15 | 217.85 | 215.00 | 249.51 |
| Lower break even point | 17914.85 | 17832.15 | 17685.00 | 17500.49 |
| Upper break even point | 18385.15 | 18267.85 | 18115.00 | 17999.51 |
| Risk/reward ratio | 3.18 | 3.97 | 4.73 | 4.54 |
| Remarks | looks like moderate | looks like moderate | break even point is very close to spot price | break even point is very close to spot price |
According to above table, best combination is 1-slightly OTM+2-OTM.
For spread= 300, and call ratio= 0.667,
| Generalization | 2-OTM+3-OTM | 2-ATM+3-OTM | 2-ITM+3-OTM | 2-ITM+3-ATM |
| 2-LK | 17850 | 17750 | 17600 | 17450 |
| 3-HK | 18150 | 18050 | 17900 | 17750 |
| Spread | 300 | 300 | 300 | 300 |
| LK-PP | 114.05 | 167.85 | 268.20 | 386.10 |
| HK-PR | 24.60 | 42.85 | 91.60 | 167.85 |
| Net debit/credit (-2*PP+3*PR) | -154.30 | -207.15 | -261.60 | -268.65 |
| Max loss (at upper range=19131.89) | -536.19 (unlimited) | -689.04 (unlimited) | -893.49 (unlimited) | -1050.54 (unlimited) |
| Max profit | 445.70 | 392.85 | 338.40 | 331.35 |
| Lower break even point | 17927.15 | 17853.575 | 17730.80 | 17584.325 |
| Upper break even point | 18595.70 | 18442.85 | 18238.40 | 18081.35 |
| Risk/reward ratio | 1.2 | 1.75 | 2.64 | 3.17 |
| Remarks | looks like moderate | looks like moderate | break even point is very close to spot price | break even point is very close to spot price |
According to above table, best combination is 1-slightly OTM+2-OTM,
And the best call ratio is 0.667, because of upper break even point is higher than upper break even point of call ratio 0.5, but the net debit is less. So if the spot price is going to fall in the time frame, then take a strike combination with a call ratio of 0.5.
Call ratio is not the main point of discussion if the spot price will move higher in near term then higher call ratio should be chosen. Similarly, if the spot price has more chances of falling in the near term till expiry, then a lower call ratio should be chosen.
For the selection of spread, we have seen that lower spread has lower upper break even point and higher spread has higher upper break even point, so if the spot price is likely to move to maximum value in the near term. Then the higher spread should be chosen.
Here we do not want to go in confusion. So we are taking 200 spread, and 0.5 Call ratio, with combination of 1-slightly OTM+2-OTM.
Trade setup for a call ratio spread:
Call ratio= 0.5, Spread= 200,
| Leg | Option type | Moneyness | Position | Quantity | Strike price (K) | Premium (P) | Premium type |
| Leg 1 | CE | slightly OTM (LK) | Buy | 1 | 17850/- | 114.05/- | Premium paid (PP) |
| Leg 2 | CE | OTM (HK) | Sell | 2 | 18050/- | 42.85/- | Premium received (PR) |
| Net premium paid/received | -28.35 | -PP+2*PR |
After taking position in both leg in a same time, price can move any direction on expiry so we check for various spot price on expiry to get sense of strategy pay offs.
Scenario 1- Spot price expires at below the lower strike price at (S) 17750/-
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= P&L for leg 1 + P&L for leg 2
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= Qty*(max(S-LK,0) – PP) + Qty*(PR – max(S-HK,0))
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 1*(max(17750-17850,0) – 114.05) + 2*(42.85 – max(17750-18050,0))
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= (max(-100,0) – 114.05) + 2*(42.85 – max(-300,0))
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= (0 -114.05) + 2*(42.85 – 0)
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= -114.05 + 2*42.85
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= -114.05 + 85.7
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= -28.35/-
Scenario 2- Spot price expires at the lower strike price at (S) 17850/-
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= P&L for leg 1 + P&L for leg 2
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= Qty*(max(S-LK,0) – PP) + Qty*(PR – max(S-HK,0))
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 1*(max(17850-17850,0) – 114.05) + 2*(42.85 – max(17850-18050,0))
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= (max(0,0) – 114.05) + 2*(42.85 – max(-200,0))
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= (0 -114.05) + 2*(42.85 – 0)
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= -114.05 + 2*42.85
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= -114.05 + 85.7
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= -28.35/-
Scenario 3- Spot price expires at the lower strike price plus net debit at (S) 17878.35/-
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= P&L for leg 1 + P&L for leg 2
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= Qty*(max(S-LK,0) – PP) + Qty*(PR – max(S-HK,0))
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 1*(max(17878.35-17850,0) – 114.05) + 2*(42.85 – max(17878.35-18050,0))
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= (max(28.35,0) – 114.05) + 2*(42.85 – max(-171.65,0))
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= (28.35 -114.05) + 2*(42.85 – 0)
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= -85.7 + 2*42.85
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= -85.7+ 85.7
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 0.00/-
Scenario 4- Spot price expires at the higher strike price at (S) 18050/-
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= P&L for leg 1 + P&L for leg 2
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= Qty*(max(S-LK,0) – PP) + Qty*(PR – max(S-HK,0))
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 1*(max(18050-17850,0) – 114.05) + 2*(42.85 – max(18050-18050,0))
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= (max(200,0) – 114.05) + 2*(42.85 – max(0,0))
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= (200 -114.05) + 2*(42.85 – 0)
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 85.95 + 2*42.85
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 85.95+ 85.7
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 171.65/-
Scenario 5- Spot price expires at the higher strike price plus max profit at (S) 18221.65/-
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= P&L for leg 1 + P&L for leg 2
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= Qty*(max(S-LK,0) – PP) + Qty*(PR – max(S-HK,0))
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 1*(max(18221.65-17850,0) – 114.05) + 2*(42.85 – max(18221.65-18050,0))
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= (max(371.65,0) – 114.05) + 2*(42.85 – max(171.65,0))
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= (371.65 -114.05) + 2*(42.85 – 171.65)
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 257.6 + 2*(-128.8)
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 257.6 – 257.6
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 0.00/-
Scenario 6- Spot price expires at above the higher strike price plus max profit at (S) 18350/-
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= P&L for leg 1 + P&L for leg 2
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= Qty*(max(S-LK,0) – PP) + Qty*(PR – max(S-HK,0))
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 1*(max(18350-17850,0) – 114.05) + 2*(42.85 – max(18350-18050,0))
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= (max(500,0) – 114.05) + 2*(42.85 – max(300,0))
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= (500 -114.05) + 2*(42.85 – 300)
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 385.95 + 2*(-257.15)
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 257.6 – 514.3
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= -256.7/-
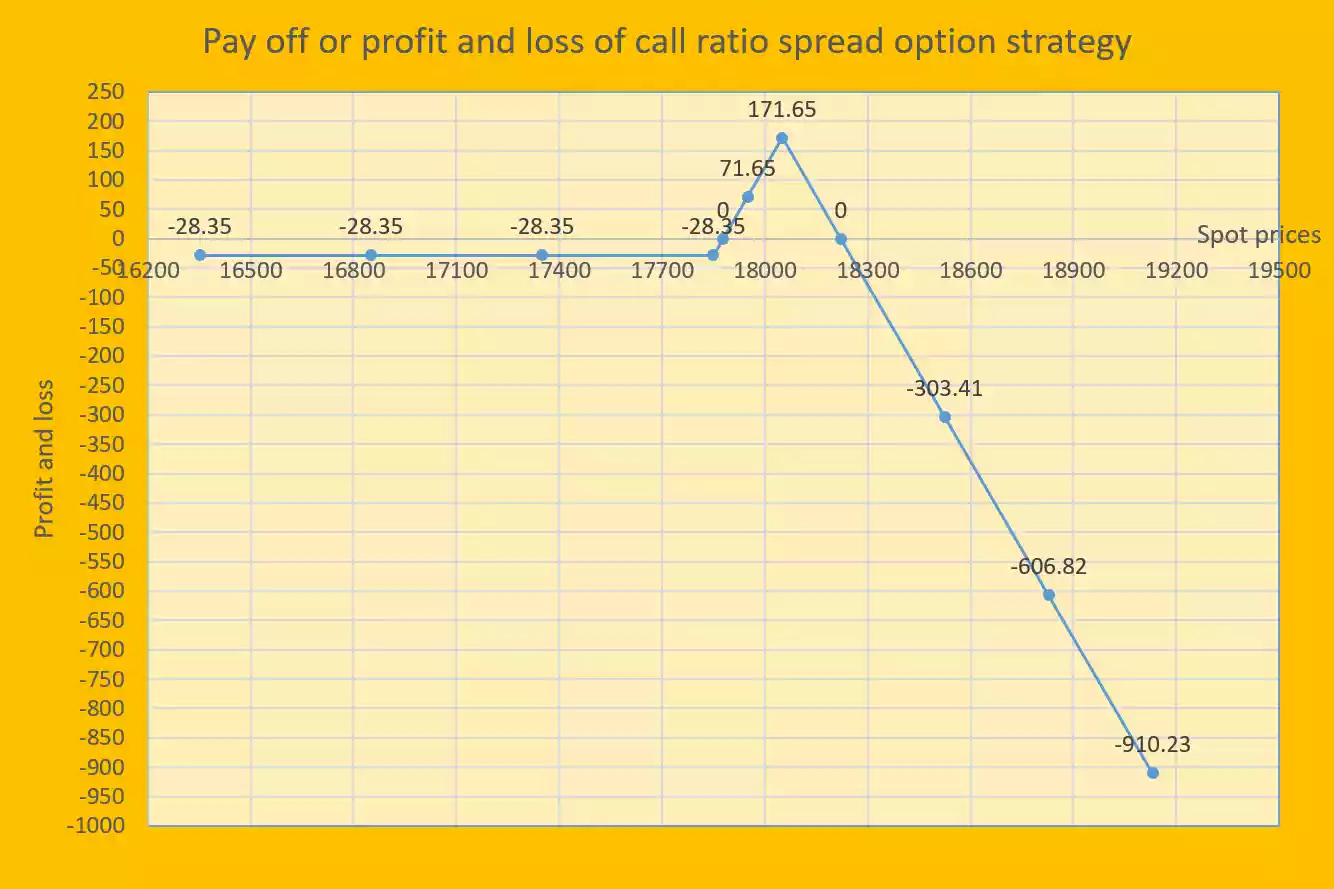
We have seen that when spot price expires at lower strike or below the lower strike then maximum loss is equal to net premium paid (-28.35/-). And when spot price expires at higher strike then maximum profit is equal to 171.65/-, means this profit is equal to difference between strike prices minus net premium paid. And when spot price expires at above higher strike plus max profit (171.65/-) Then the loss starts from here and the higher the spot price rises, the higher the loss
Strategy generalization for a call ratio spread option strategy:
Spread= Difference between the higher strike and lower strike price
Spread= 18050-17850
Spread= 200
Net debit/credit= – lower strike qty*premium paid for lower strike + higher strike qty*premium received for higher strike
Note- If the result is negative then net debit if the result is positive then net credit.
Net debit/credit= -1*114.05+2*42.85
Net debit/credit= -114.05+85.7
Net debit= -28.35/-
Max profit= lower strike qty*spread + net debit/credit
Max profit= 1*200 – 28.35
Max profit= 171.65/-
Lower break even point= lower strike price + ABS(net debit/lower strike qty)
Where, ABS stands for absolute value, and qty stands for quantity.
Note- In a net credit, lower break even point will be not applicable.
Lower break even point= 17850 + ABS(-28.35/1)
Lower break even point= 17850 + 28.35
Lower break even point= 17878.35/–
Upper break even point= higher strike price + max profit/(higher strike qty-lower strike qty)
Upper break even point= 18050 + 171.65/(2-1)
Upper break even point= 18050 + 171.65
Upper break even point= 18221.65/–
Max loss= Upper break even point – Upper range
Where Upper range= expected spot price rise till expiry
Here we take upper range= Current spot price+ 2*SD*current spot price
If annual SD=20%, and expiry days= 14,
Upper range (2SD)= 17742+2*17742*(20/100)*√(14/365)= 19131.88/-
Max loss= 18221.65-19131.88
Max loss= -910.23/-
Max profit at most strike price= at higher strike
Max profit at most strike price= 18050/-
Max loss at spot price= at above upper break even point same as upper range
Max loss at spot price= 19131.88/-
Strategy pay off (P&L) table for call ratio spread option strategy:
Strategy pay off or profit and loss of call ratio spread option strategy is combined profit and loss of leg 1 and leg 2 positions for various spot prices on expiry.
Use calculator for calculation of pay off schedule or profit and loss:
Pay of schedule:
| Various spot prices on expiry (Sf) | Pay off or profit and loss of strategy |
| 16352.10 | -28.35 |
| 16851.40 | -28.35 |
| 17350.70 | -28.35 |
| 17850 | -28.35 |
| 17878.35 | 0 |
| 17950 | 71.65 |
| 18050 | 171.65 |
| 18221.65 | 0 |
| 18525.06 | -303.41 |
| 18828.47 | -606.82 |
| 19131.88 | -910.23 |
Strategy pay off (P&L) chart for call ratio spread option strategy:
Strategy pay off chart is the presentation of profit and loss on y-axis and various spot prices on x-axis.
Why should I use this call ratio spread option strategy?
If using Bull call spread option strategy then you will have to pay more net debit than call ratio spread option strategy and also get less profit from this strategy. But the loss of this strategy is limitless. So if your expected spot price upper limit is below the upper break even point then definitely use call ratio spread option strategy as profit potential is better than bull call spread option strategy.
Call ratio spread option strategy Greeks:
Option strategy Greeks is the sum of leg 1 option contract Greeks and leg 2 option contract Greeks.
Below is the call ratio spread option strategy Greeks snapshot, for leg 1 and leg 2 positions-
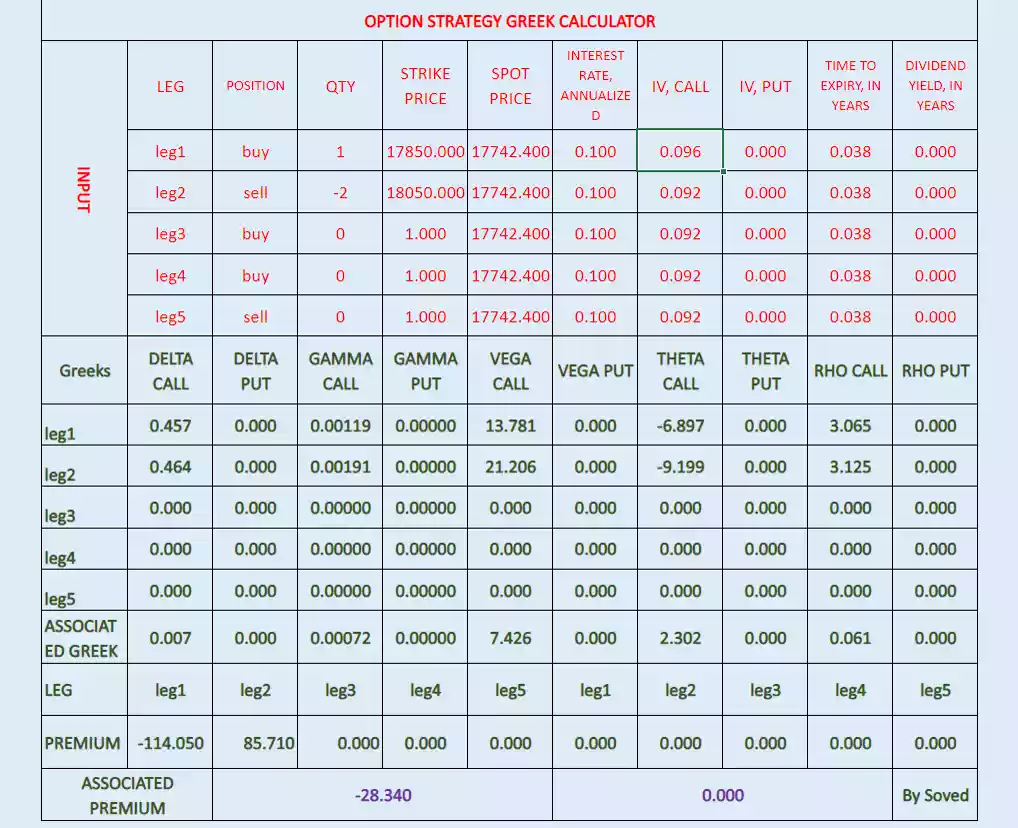
Here are the Greeks associated with a call ratio spread option strategy:
Delta and Gamma:
Associated Delta= 0.007
If unit increase in spot price for 1Rs.,
Then, associated premium= old premium + associated Delta
associated premium= -28.34 + 0.007= -28.333
But associated premium by Soved option strategy Greek calculator is -28.332.
this difference due to change in Delta. And change in Delta occurred by Gamma.
Associated Gamma= 0.00072
Associated delta= old Delta + associated Gamma
Associated delta= 0.007 + 0.00072
Associated delta= 0.00772~0.008
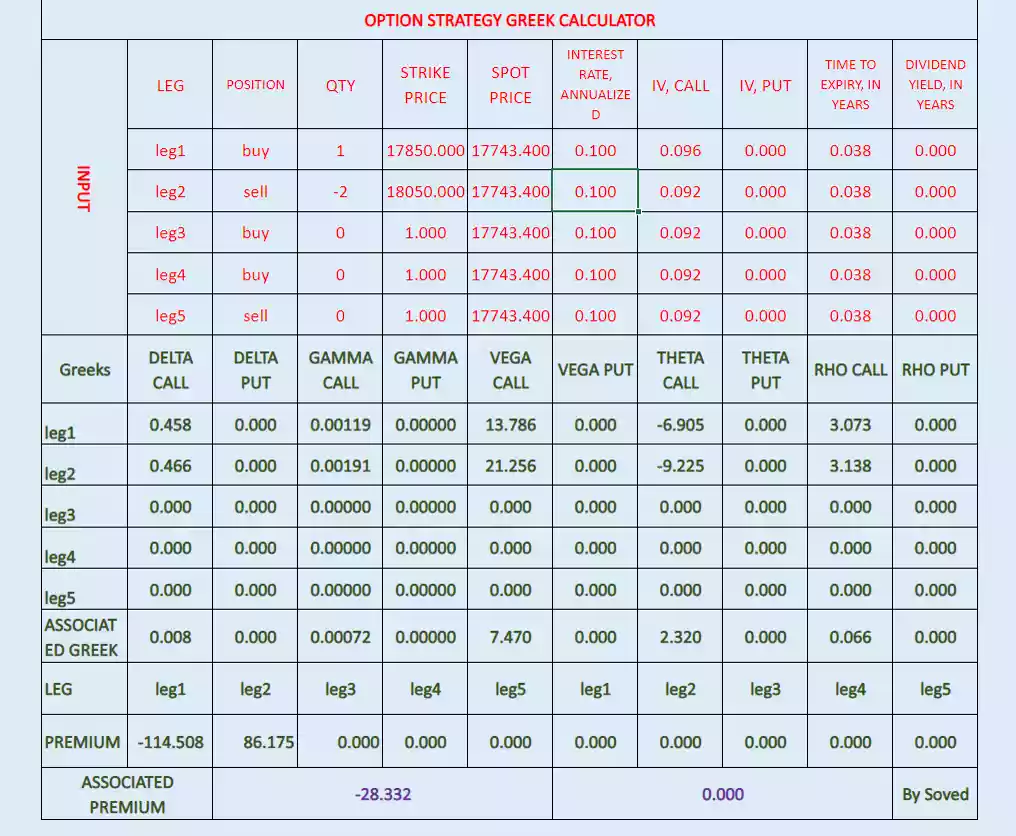
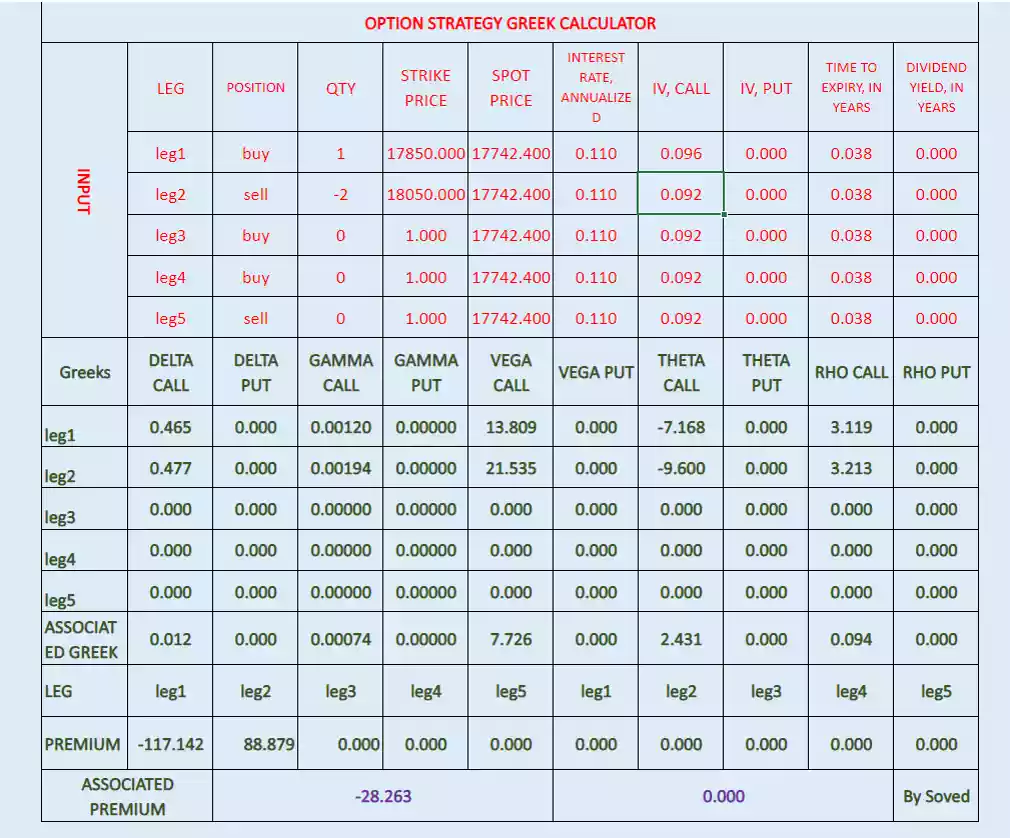
Compare it by below image which is calculated option Greeks and associated premium by unit change in spot price-
Theta:
Associated Theta= 2.302
Old associated premium= 28.334
After 1day change (decrease) in expiry days,
Then, new associated premium= old associated premium – associated Theta
Negative sign for decrease in time,
New associated premium= -28.334 – 2.302
New associated premium= -30.636
check it below image found some error. This error due to After 1 day change in time then associated Theta also change.
So, Associated Theta after 1 day decrease in time is= 2.073
Then average associated theta is= (2.302+2.073)/2= 2.1875
So now, new associated premium= old associated premium – associated Theta
New associated premium= -28.334 – 2.1875
New associated premium= -30.5215
Check it, Its almost correct. Now difference due to Theta not change as a symmetrical its change in function.
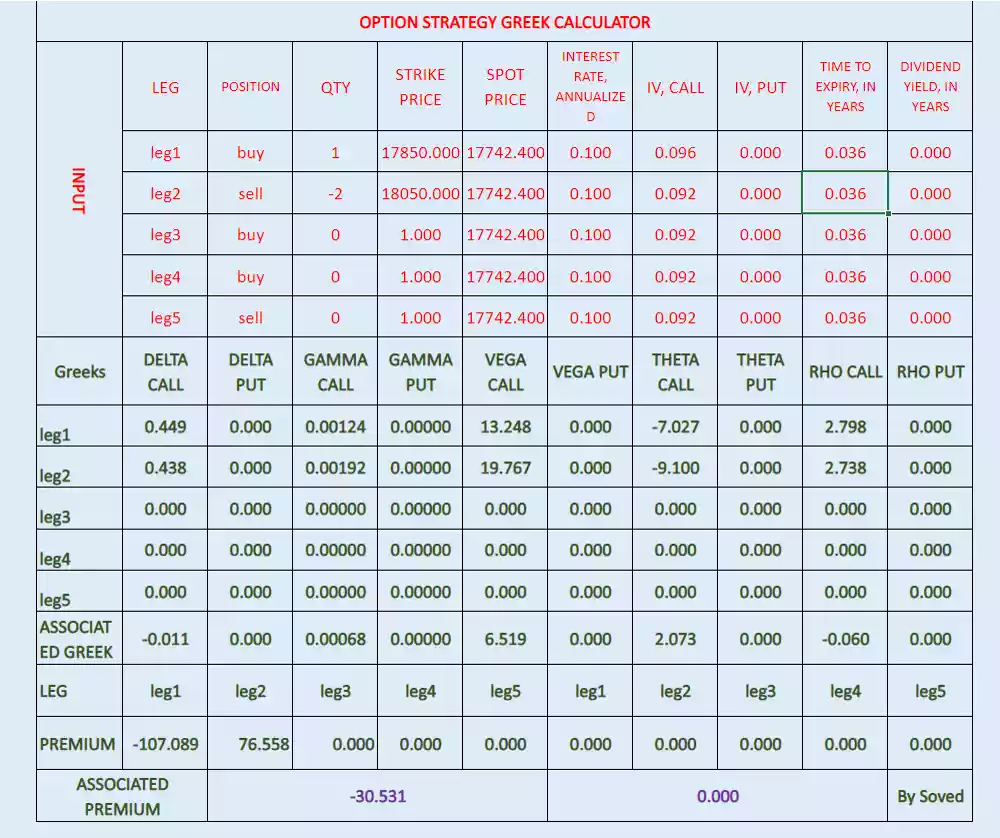
Vega:
Associated Vega= 7.426
Associated Vega after 1% implied volatility increase= 8.523
Average associated Vega= (7.426+8.523)/2= 7.9745
So, associated new premium= associated old premium + average associated Vega
Associated new premium= -28.334 + 7.9745
Associated new premium= -20.3595
Check it in below image some change due to functional change in associated Vega after change in implied volatility.
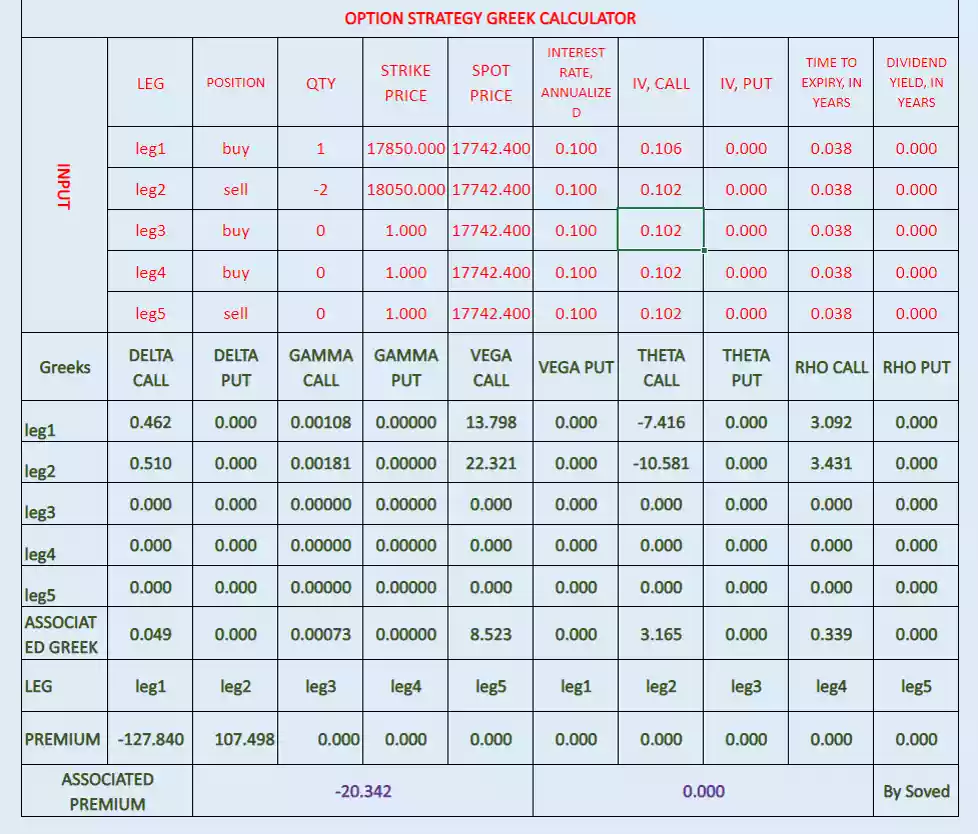
Rho:
Associated Rho= 0.061
Associated Rho after 1% interest rate increase= 0.094 (note-value by below image)
Average associated Rho= (0.061+0.094)/2= 0.0775
So, associated new premium= associated old premium + average associated Rho
Associated new premium= -28.334 + 0.0775
Associated new premium= -28.2565
Check it in below image some change due to functional change in associated Rho after change in interest rate.
All associated option Greeks will not be the same during the life of the option, it will change from change in option pricing variables.
Overall, a call ratio spread is a unlimited-risk, limited-reward options strategy that can be used to profit from a limited bullish range (up to higher strike) in the underlying asset. But according to Associated Option Greeks, gains and losses don’t happen overnight, it takes time to expire. But due to high value of Vega it will be very sensitive.
Call ratio back spread option strategy:
The strategy is implemented when one is completely bullish on a stock or index. When you apply the call ratio back spread, you get an unlimited profit if the market goes up, a limited profit if the market goes down, and a predetermined loss if the market stays within a range. It is posted to the net credit account.
Strategy notes for a call ratio back spread option strategy:
The call ratio back spread option strategy is a 2 leg option strategy with different quantity as it involves selling one or two ITM (lower strike) call options and buying two or three OTM (higher strike) call options.
To implement call ratio spread-
Leg 1- Sell 1-ITM (LK-lower strike) call option
Leg 2- Buy 2-OTM (HK-higher strike) call option
Or
Leg 1- Sell 2-ITM (LK-lower strike) call option
Leg 2- Buy 3-OTM (HK-higher strike) call option
When take positions ensure that both leg option contracts should be same underlying asset, same expiry date, and with different quantity of options. Also ensure that when you take position in both leg then take position in both leg same time.
Example of call ratio back spread option strategy:
For a example of call ratio back spread option strategy, we are taking Nifty options contract.

Option contract- Nifty 27Apr … CE
Today’s date- 13/04/2023
Expiry date- 27/04/2023
Expiry days= expiry date – todays date= 14days
Underlying asset- Nifty 50
Directional view/outlook- Bullish
Spot price (S)- 17742/-
Annual historical volatility- 20%
Upper range (2SD)= 17742+2*17742*(20/100)*√(14/365)= 19131.88/-
Spread and strike price selection for a call ratio back spread option strategy:
In the table below, we will look at different spreads and different strike combinations to see which one is better. And also we will compare with call ratio of 0.5 and 0.667.
For spread= 100, and call ratio= 0.5,
| Generalization | 1-OTM+2-OTM | 1-ATM+2-OTM | 1-ITM+2-OTM | 1-ITM+2-ATM |
| 1-LK | 17850 | 17750 | 17700 | 17650 |
| 2-HK | 17950 | 17850 | 17800 | 17750 |
| Spread | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| LK-PR | 114.05 | 167.85 | 198.05 | 230.95 |
| HK-PP | 72 | 114.05 | 138.95 | 167.85 |
| Net debit/credit (PR-2*PP) | -29.95 | -60.25 | -79.85 | -104.75 |
| Max profit (at upper range=19131.89) | 1051.94 (unlimited) | 1121.64 (unlimited) | 1152.04 (unlimited) | 1177.14 (unlimited) |
| Max loss | -129.95 | -160.25 | -179.85 | -204.75 |
| Lower break even point | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Upper break even point | 18079.95 | 18010.25 | 17979.85 | 17954.75 |
| Risk/reward ratio | 0.12 | 0.14 | 0.16 | 0.17 |
| Remarks | break even point is very far to spot price | break even point is very far to spot price | looks like moderate | risk reward ratio is high |
N/A means Not Applicable, the lower break even point will not apply when the strike combination creates a net debit.
As per the above table, the best combination is 1-ITM+2-OTM, but don’t choose it due to net debit.
For spread= 100, and call ratio= 0.667,
| Generalization | 2-OTM+3-OTM | 2-ATM+3-OTM | 2-ITM+3-OTM | 2-ITM+3-ATM |
| 2-LK | 17850 | 17750 | 17700 | 17650 |
| 3-HK | 17950 | 17850 | 17800 | 17750 |
| Spread | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| LK-PR | 114.05 | 167.85 | 198.05 | 230.95 |
| HK-PP | 72 | 114.05 | 138.95 | 167.85 |
| Net debit/credit (2*PR-3*PP) | 12.10 | -6.45 | -20.75 | -41.65 |
| Max profit (at upper range=19131.89) | 993.99 (unlimited) | 1075.44 (unlimited) | 1111.14 (unlimited) | 1140.24 (unlimited) |
| Max loss | -187.9 | -206.45 | -220.75 | -241.65 |
| Lower break even point | 17856.05 | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Upper break even point | 18137.9 | 18056.45 | 18020.75 | 17991.65 |
| Risk/reward ratio | 0.19 | 0.19 | 0.2 | 0.21 |
| Remarks | break even point is very far to spot price | break even point is very far to spot price | looks like moderate | risk reward ratio is high |
According to above table, best combination is 2-ITM+3-OTM, but don’t choose it due to net debit.
And the best call ratio is 0.5, because of upper break even point is lesser than upper break even point of call ratio 0.667, but the net debit is more. So if the spot price is going to fall in the time frame, then take a strike combination with a call ratio of 0.667.
For spread= 200, and call ratio= 0.5,
| Generalization | 1-OTM+2-OTM | 1-ATM+2-OTM | 1-ITM+2-OTM | 1-ITM+2-ATM |
| 1-LK | 17850 | 17750 | 17650 | 17550 |
| 2-HK | 18050 | 17950 | 17850 | 17750 |
| Spread | 200 | 200 | 200 | 200 |
| LK-PR | 114.05 | 167.85 | 230.95 | 306.25 |
| HK-PP | 42.85 | 72.0 | 114.05 | 167.85 |
| Net debit/credit (PR-2*PP) | 28.35 | 23.85 | 2.85 | -29.45 |
| Max profit (at upper range=19131.89) | 910.24 (unlimited) | 1005.74 (unlimited) | 1084.74 (unlimited) | 1152.44 (unlimited) |
| Max loss | -171.65 | -176.15 | -197.15 | -229.45 |
| Lower break even point | 17878.35 | 17773.85 | 17652.85 | N/A |
| Upper break even point | 18221.65 | 18126.15 | 18047.15 | 17979.45 |
| Risk/reward ratio | 0.19 | 0.175 | 0.182 | 0.2 |
| Remarks | break even point is very far to spot price | looks like moderate | looks like moderate | risk reward ratio is high |
According to above table, best combination is 1-ITM+2-OTM.
For spread= 200, and call ratio= 0.667,
| Generalization | 2-OTM+3-OTM | 2-ATM+3-OTM | 2-ITM+3-OTM | 2-ITM+3-ATM |
| 2-LK | 17850 | 17750 | 17650 | 17550 |
| 3-HK | 18050 | 17950 | 17850 | 17750 |
| Spread | 200 | 200 | 200 | 200 |
| LK-PR | 114.05 | 167.85 | 230.95 | 306.25 |
| HK-PP | 42.85 | 72 | 114.05 | 167.85 |
| Net debit/credit (2*PR-3*PP) | 99.55 | 119.7 | 119.75 | 108.95 |
| Max profit (at upper range=19131.89) | 781.44 (unlimited) | 901.59 (unlimited) | 1001.64 (unlimited) | 1090.84 (unlimited) |
| Max loss | -300.45 | -280.3 | -280.25 | -291.05 |
| Lower break even point | 17899.775 | 17809.85 | 17709.875 | 17604.475 |
| Upper break even point | 18350.45 | 18230.3 | 18130.25 | 18041.05 |
| Risk/reward ratio | 0.384 | 0.311 | 0.280 | 0.267 |
| Remarks | break even point is very far to spot price | break even point is very far to spot price | looks like moderate | max loss is high |
According to above table, best combination is 2-ITM+3-OTM,
And the best call ratio is 0.5, because of upper break even point is lesser than upper break even point of call ratio 0.667, but the net credit is more. So if the spot price is going to fall in the time frame, then take a strike combination with a call ratio of 0.667.
For spread= 300, and call ratio= 0.5,
| Generalization | 1-OTM+2-OTM | 1-ATM+2-OTM | 1-ITM+2-OTM | 1-ITM+2-ATM |
| 1-LK | 17850 | 17750 | 17600 | 17450 |
| 2-HK | 18150 | 18050 | 17900 | 17750 |
| Spread | 300 | 300 | 300 | 300 |
| LK-PR | 114.05 | 167.85 | 268.20 | 386.19 |
| HK-PP | 24.60 | 42.85 | 91.60 | 167.85 |
| Net debit/credit (PR-2*PP) | 64.85 | 82.15 | 85.00 | 50.49 |
| Max profit (at upper range=19131.89) | 746.74 (unlimited) | 864.04 (unlimited) | 1016.89 (unlimited) | 1132.38 (unlimited) |
| Max loss | -235.15 | -217.85 | -215.00 | -249.51 |
| Lower break even point | 17914.85 | 17832.15 | 17685.00 | 17500.49 |
| Upper break even point | 18385.15 | 18267.85 | 18115.00 | 17999.51 |
| Risk/reward ratio | 0.315 | 0.252 | 0.211 | 0.220 |
| Remarks | break even point is very far to spot price | break even point is very far to spot price | looks like moderate | max loss is high |
According to above table, best combination is 1-ITM+2-OTM.
For spread= 300, and call ratio= 0.667,
| Generalization | 2-OTM+3-OTM | 2-ATM+3-OTM | 2-ITM+3-OTM | 2-ITM+3-ATM |
| 2-LK | 17850 | 17750 | 17600 | 17450 |
| 3-HK | 18150 | 18050 | 17900 | 17750 |
| Spread | 300 | 300 | 300 | 300 |
| LK-PR | 114.05 | 167.85 | 268.20 | 386.10 |
| HK-PP | 24.60 | 42.85 | 91.60 | 167.85 |
| Net debit/credit (2*PR-3*PP) | 154.30 | 207.15 | 261.60 | 268.65 |
| Max profit (at upper range=19131.89) | 536.19 (unlimited) | 689.04 (unlimited) | 893.49 (unlimited) | 1050.54 (unlimited) |
| Max loss | -445.70 | -392.85 | -338.40 | -331.35 |
| Lower break even point | 17927.15 | 17853.575 | 17730.80 | 17584.325 |
| Upper break even point | 18595.70 | 18442.85 | 18238.40 | 18081.35 |
| Risk/reward ratio | 0.831 | 0.570 | 0.379 | 0.315 |
| Remarks | break even point is very far to spot price | break even point is very far to spot price | looks like moderate | looks like moderate |
According to above table, best combination is 2-ITM+3-ATM or 2-ITM+3-OTM,
And the best call ratio is 0.5, because of upper break even point is lesser than upper break even point of call ratio 0.667, but the net credit is more. So if the spot price is going to fall in the time frame, then take a strike combination with a call ratio of 0.667.
For the selection of spread, we have seen that lower spread has net debit and higher spread has net credit so we will choose higher spread for initially receive net credit.
Here we do not want to go in confusion. So we are taking 200 spread, and 0.667 Call ratio, with combination of 2-ITM+3-slightly OTM.
Trade setup for a call ratio back spread:
Call ratio= 0.667, Spread= 200,
| Leg | Option type | Moneyness | Position | Quantity | Strike price (K) | Premium (P) | Premium type |
| Leg 1 | CE | ITM (LK) | Sell | 2 | 17650/- | 230.95/- | Premium received (PR) |
| Leg 2 | CE | slightly OTM (HK) | Buy | 3 | 17850/- | 114.05/- | Premium paid (PP) |
| Net premium paid/received | 119.75/- | 2*PR-3*PP |
After taking position in both leg in a same time, price can move any direction on expiry so we check for various spot price on expiry to get sense of strategy pay offs.
Scenario 1- Spot price expires at below the lower strike price at (S) 17550/-
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= P&L for leg 1 + P&L for leg 2
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= Qty*(PR – max(S-LK,0)) + Qty*(max(S-HK,0) – PP)
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 2*(230.95 – max(17550-17650,0)) + 3*(max(17550-17850,0) – 114.05)
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 2*(230.95 – max(-100,0)) + 3*(max(-300,0) – 114.05)
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 2*(230.95 – 0) + 3*(0 – 114.05)
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 2*230.95 + 3*(-114.05)
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 461.9 – 342.15
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 119.75/-
Scenario 2- Spot price expires at the lower strike price at (S) 17650/-
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= P&L for leg 1 + P&L for leg 2
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= Qty*(PR – max(S-LK,0)) + Qty*(max(S-HK,0) – PP)
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 2*(230.95 – max(17650-17650,0)) + 3*(max(17650-17850,0) – 114.05)
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 2*(230.95 – max(0,0)) + 3*(max(-200,0) – 114.05)
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 2*(230.95 – 0) + 3*(0 – 114.05)
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 2*230.95 + 3*(-114.05)
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 461.9 – 342.15
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 119.75/-
Scenario 3- Spot price expires at the lower strike price plus 0.5*net credit at (S) 17709.875/-
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= P&L for leg 1 + P&L for leg 2
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= Qty*(PR – max(S-LK,0)) + Qty*(max(S-HK,0) – PP)
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 2*(230.95 – max(17709.875-17650,0)) + 3*(max(17709.875-17850,0) – 114.05)
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 2*(230.95 – max(59.875,0)) + 3*(max(-140.125,0) – 114.05)
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 2*(230.95 – 59.875) + 3*(0 – 114.05)
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 2*171.075 + 3*(-114.05)
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 342.15 – 342.15
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 0/-
Scenario 4- Spot price expires at the higher strike price at (S) 17850/-
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= P&L for leg 1 + P&L for leg 2
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= Qty*(PR – max(S-LK,0)) + Qty*(max(S-HK,0) – PP)
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 2*(230.95 – max(17850-17650,0)) + 3*(max(17850-17850,0) – 114.05)
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 2*(230.95 – max(200,0)) + 3*(max(0,0) – 114.05)
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 2*(230.95 – 200) + 3*(0 – 114.05)
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 2*30.95 + 3*(-114.05)
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 61.9 – 342.15
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= -280.25/-
Scenario 5- Spot price expires at the higher strike price plus max loss at (S) 18130.25/-
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= P&L for leg 1 + P&L for leg 2
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= Qty*(PR – max(S-LK,0)) + Qty*(max(S-HK,0) – PP)
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 2*(230.95 – max(18130.25-17650,0)) + 3*(max(18130.25-17850,0) – 114.05)
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 2*(230.95 – max(480.25,0)) + 3*(max(280.25,0) – 114.05)
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 2*(230.95 – 480.25) + 3*(280.25 – 114.05)
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 2*(-249.3) + 3*166.2
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= -498.6 + 498.6
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 0.00/-
Scenario 6- Spot price expires at above the higher strike price plus max profit at (S) 18350/-
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= P&L for leg 1 + P&L for leg 2
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= Qty*(PR – max(S-LK,0)) + Qty*(max(S-HK,0) – PP)
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 2*(230.95 – max(18350-17650,0)) + 3*(max(18350-17850,0) – 114.05)
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 2*(230.95 – max(700,0)) + 3*(max(500,0) – 114.05)
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 2*(230.95 – 700) + 3*(500 – 114.05)
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 2*(-469.05) + 3*385.95
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= -938.1 + 1157.85
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 219.75/-
We have seen that when spot price expires at lower strike or below the lower strike then profit is equal to net premium received (119.75/-). And when spot price expires at higher strike then maximum loss is equal to -280.25/-, means this loss is equal to twice of difference between strike prices minus net premium received. And when spot price expires at above higher strike plus max loss (280.25/-) Then the profit starts from here and the higher the spot price rises, the higher the profit
Strategy generalization for a call ratio back spread option strategy:
Spread= Difference between the higher strike and lower strike price
Spread= 17850 – 17650
Spread= 200
Net debit/credit= lower strike qty*premium received for lower strike – higher strike qty*premium paid for higher strike
Note- If the result is negative then net debit if the result is positive then net credit.
Net debit/credit= 2*230.95 – 3*114.05
Net debit/credit= 461.90 – 342.15
Net debit= 119.75/-
Max loss= -lower strike qty*spread + net debit/credit
Max loss= -2*200 + 119.75
Max loss= -280.25/-
Lower break even point= lower strike price + net credit/lower strike qty
Note- In a net debit, lower break even point will be not applicable.
Lower break even point= 17650 + 119.75/2
Lower break even point= 17650 + 59.875
Lower break even point= 17709.875/–
Upper break even point= higher strike price + ABS(max loss)/(higher strike qty-lower strike qty)
Where, ABS stands for absolute value, and qty stands for quantity.
Upper break even point= 17850 + ABS(-280.25)/(3-2)
Upper break even point= 17850 + 280.25
Upper break even point= 18130.25/–
Max profit= Upper range – Upper break even point
Where Upper range= expected spot price rise till expiry
Here we take upper range= Current spot price+ 2*SD*current spot price
If annual SD=20%, and expiry days= 14,
Upper range (2SD)= 17742+2*17742*(20/100)*√(14/365)= 19131.88/-
Max profit= 19131.88 – 18130.25
Max profit= 1001.63/-
Max profit at spot price= at above upper break even point same as upper range
Max profit at spot price= 19131.88
Max loss at spot price= at higher strike price
Max loss at spot price= 17850/-
Strategy pay off (P&L) table for call ratio back spread option strategy:
Strategy pay off or profit and loss of call ratio back spread option strategy is combined profit and loss of leg 1 and leg 2 positions for various spot prices on expiry.
Use calculator for calculation of pay off schedule or profit and loss:
Pay of schedule:
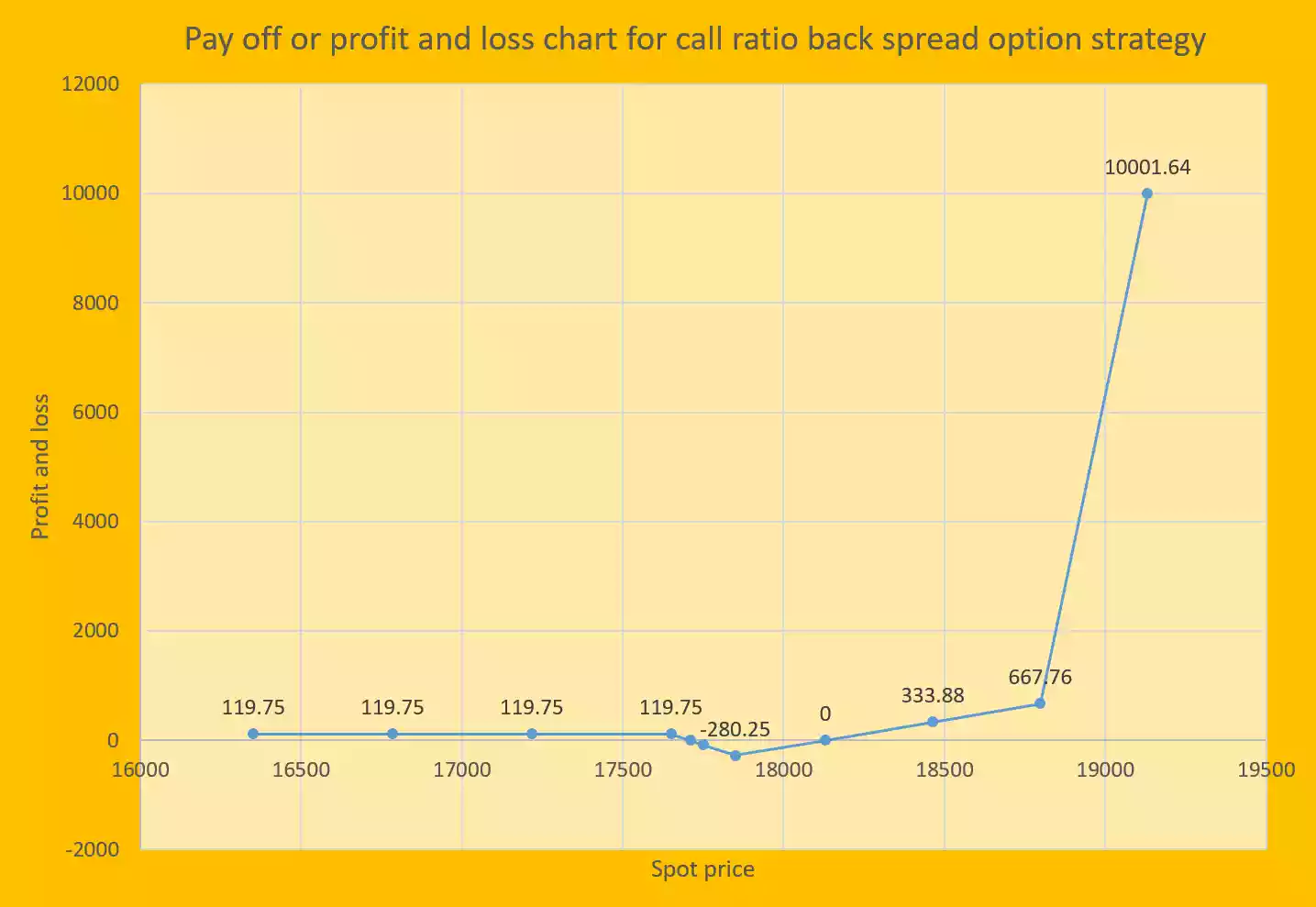
| Various spot prices on expiry (Sf) | Pay off or profit and loss of strategy |
| 16352.11 | 119.75 |
| 16784.74 | 119.75 |
| 17217.37 | 119.75 |
| 17650 | 119.75 |
| 17709.875 | 0 |
| 17750 | -80.25 |
| 17850 | -280.25 |
| 18130.25 | 0 |
| 18464.13 | 333.88 |
| 18798.01 | 667.76 |
| 19131.89 | 10001.64 |
Strategy pay off (P&L) chart for call ratio back spread option strategy:
Strategy pay off chart is the presentation of profit and loss on y-axis and various spot prices on x-axis.
Why should I use this call ratio back spread option strategy?
You should choose this strategy if you expect the spot price to move beyond the range of Upper Break Even Point and Lower Break Even Point to any side.
Call ratio back spread option strategy Greeks:
Option strategy Greeks is the sum of leg 1 option contract Greeks and leg 2 option contract Greeks.
Below is the call ratio back spread option strategy Greeks snapshot, for leg 1 and leg 2 positions-
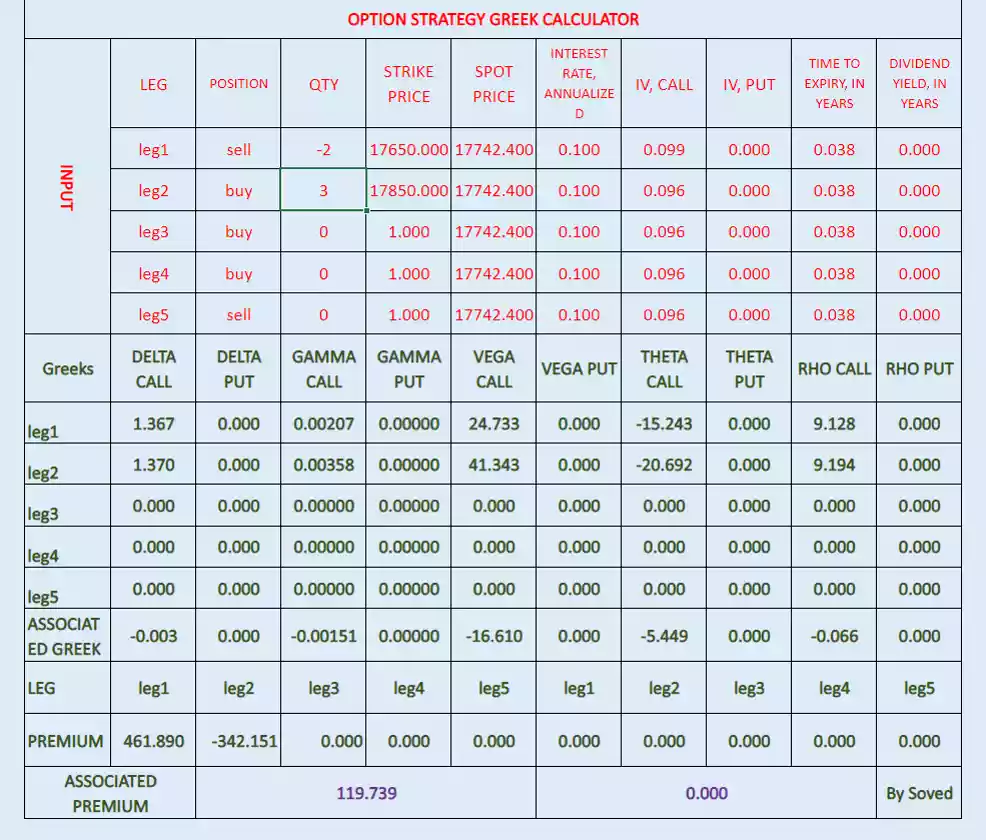
Above image displayed calculated associated option strategy Greeks by Soved option strategy Greek calculator.
So, Associated Delta= -0.003
Associated Gamma= -0.00151
Associated Vega= -16.61
Associated Theta= -5.449
Associated Rho= -0.066
Associated old premium= 119.739
Below image displayed 1Rs. increase in spot price, 0.01 increase in implied volatility, and 1/365 decrease in time to expiry days.
So, Associated Delta= -0.026
Associated Gamma= -0.00137
Associated Vega= -15.584
Associated Theta= -6.2
Associated Rho= -0.202
Average associated Delta= (-0.003 -0.026)/2= -0.0145
Average associated Gamma= Its not affect direct the associated premium its affect only Delta and affected Delta(-0.026) we have taken in average associated Delta calculation.
Average associated Vega= (-16.61 -15.584)/2= -16.097
Average associated Theta= (-5.449 -6.2)/2= -5.8245
Average associated Rho= Its not affect the associated premium because of not change in interest rate.
So, New associated premium= old associated premium + average associated Delta + average associated Vega – average associated Theta
Note-average associated Theta is negative due to decrease in time.
New associated premium= 119.739 – 0.0145 – 16.097 -(-5.8245)
New associated premium= 109.452
Check it below image some difference due to functional change in option Greeks.
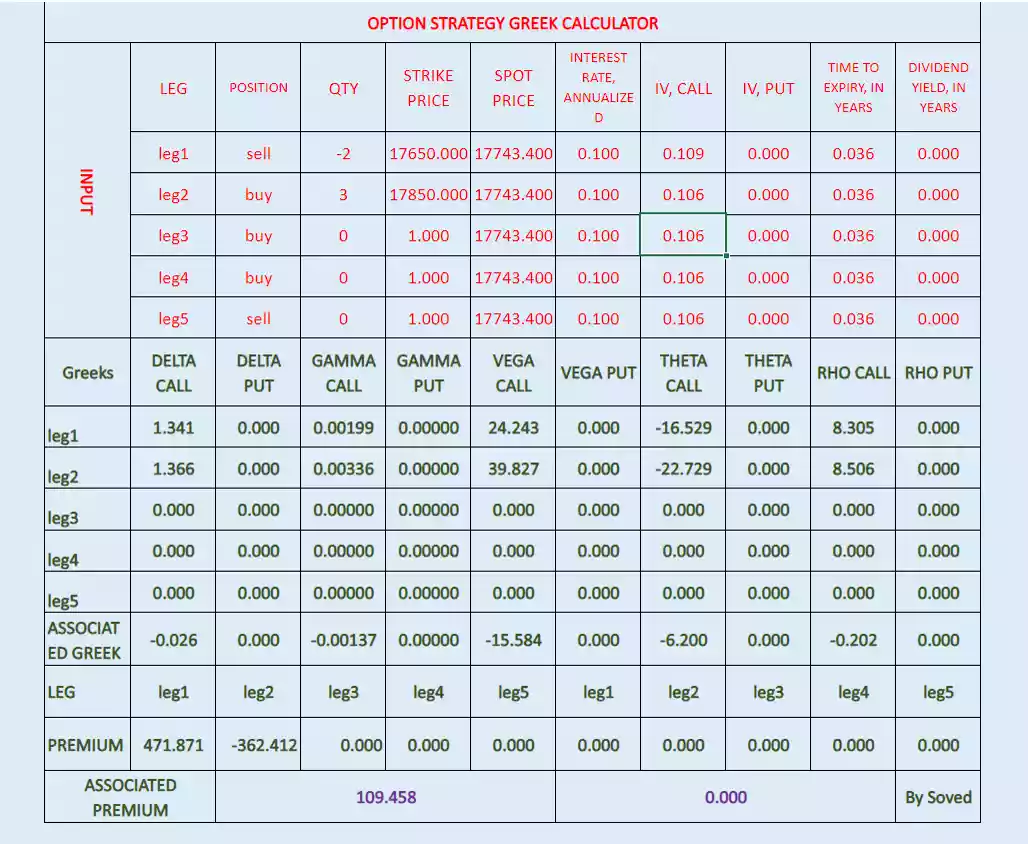
All associated option Greeks will not be the same during the life of the option, it will change from change in option price variables.
After the calculation of associated Greeks and associated premium we have understood that how is affected associated premium by associated Greeks, so careful if you are a strategy trader, but in option strategy expiry all option Greeks will be negligible so don’t care if you are a option strategy investor. In a investing option strategy you have to follow only spot price and implied volatility at entry time.
Overall, a call ratio back spread is a limited-risk, unlimited-reward option strategy that can be used to profit from a high volatile in the underlying asset. But according to Associated Option Greeks, gains and losses don’t happen overnight, it takes time to expire. But due to higher value of Vega it will be very sensitive for implied volatility.
