What is call spread option strategy?
First know about call spread option strategy, before that we have to know about option strategy. Till now we have to know about naked option strategy, where buy or sell positions taken alone without having any other position in same market or other market. But option strategy, different from naked option strategy because of in option strategy taken buy or sell position in option contract at least two positions or more than two positions or one position in option market and covered position in same market or other market.
I have understand the risk/return profiles for call naked option strategy and put naked option strategy. Now we will understand all about option strategies. Strategy means use minimum 2-leg option contract or more leg option contract by equity derivative product for taking position in same time, with same underlying asset, with same strike or different strikes, with same maturity or different maturity.
Call spread option strategy using call option contracts for taking positions. Maximum and minimum two positions taken in the call spread option strategy. In a call spread option strategy potential losses limited so as on potential profit also limited.
What is option spreads?
Spreads involve combining options on the same underlying asset and of same type (call/put) of options contract but with different strikes and maturities. These are limited profit and limited loss positions. They are primarily categorized into three sections as-
- Vertical spread
- Horizontal spread
- Diagonal spread
Vertical spread:
Vertical spread are created by using options having same expiry but different strike prices. Further, These can be created either using calls a combination or puts as combination. These can be further classified-
- Bullish vertical spread using calls (bull call spread)
- Bullish vertical spread using puts (bull put spread)
- Bearish vertical spread using calls (bear call spread)
- Bearish vertical spread using puts (bear put spread)
Horizontal spread:
Horizontal spread involves same strike, same type (call or put option contracts), but different expiry options. This is also known as time spread or calendar spread. Here it is not possible to draw the pay off chart as the expiries underlying the spread are different.
Underlying reasoning behind horizontal spread is that these two options would have different time values and the trader believes that difference between the time value of these two options would shrink or widen. This is essentially a play on premium differences between two options prices squeezing or widening.
Diagonal spread:
Diagonal spread involves combination of options having same underlying but different expiries as well as different strikes. Again as the two legs in a spread are in different maturities. It is not possible to draw pay offs here as well. There are much more complicated in nature and in execution. These strategies are more suitable for the OTC market than for the exchange traded markets.
Table of Contents
Bull call spread option strategy:
The spread option strategies are the simplest option strategies that a participants (trader/investor/arbitrager) easily implement or trade. Bull call spread option strategy used when your outlook on market moderately bullish not aggressive. Here we will understand the market outlook or directional view of underlying asset price by analysis of underlying asset such analysis as economy analysis, industry/sector analysis, technical analysis, fundamental analysis etc. With these analysis keep in mind current news and events of underlying asset and all market events.
Economy analysis:
Economic analysis is used by governments, businesses, and individuals to make informed decisions about resource allocation, investment, and policy formulation. It can be applied to different areas of the economy, such as macroeconomic analysis, microeconomic analysis, and sector-specific analysis.
For the Indian economy is the sixth-largest in the world by nominal GDP and the third-largest by purchasing power parity. Its growth rate has been slowing in recent years due to a combination of structural and cyclical factors, including the COVID-19 pandemic. However, it remains a major global economic player with significant potential for future growth.
Industry/sector analysis:
India’s economy is a diverse mix of different sectors, with services, agriculture, and industry being the three main sectors. The services sector is the largest contributor to India’s GDP, accounting for over 50% of its output, followed by agriculture at around 17%, and industry at around 30%.
Within the services sector, the largest sub-sectors are finance, trade, and public administration. Agriculture is primarily focused on food crops, while the industry sector is dominated by manufacturing, with key industries including textiles, automobiles, and pharmaceuticals. The growth and development of each sector are crucial for the overall health and stability of the Indian economy.
Fundamental analysis:
In index have several stocks so fundamental analysis not possible but for a stock fundamental analysis must do. So for stock underlying asset check all financial report such as balance sheet, profit and loss etc. Check latest quarterly result and next quarter result announcement, if result declaration date fall in your option strategy time period or remaining expiry time.
Then you know that according to management guidance upcoming quarterly result will be better than from latest quarter and better result from last year same quarter result. This is difficult to address best upcoming quarter result but address by management and news of that company, and also address upside limit of that company or stock.
Technical analysis:
For technical analysis we have to select that stock which one is in down trend and now trend is weak. In down trend of particular stock/index ensure that down trend of stock is not a bad performance or poor financial report of that company. And also check it is at a near 52 week low price of underlying asset, testing the 200 day moving average and a near support.
Given all this there is a high probability that the stock could stage a relief rally. however you are not completely bullish as whatever said and done, the stock is still in a downtrend.
Volatile range analysis:
Volatile range analysis is the sum of normal distribution of stock/index daily return in a particular time frame. For a calculation of volatile range we have to use volatility (standard deviation) of underlying asset.
Volatility range is the range of underlying asset price which says that stock/index (underlying asset) price will vary between calculated price range of particular underlying asset by volatility (SD).
Underlying asset price range for a particular time, calculation formula is-
Upper range of stock/index for a T time= current price + current price*(SD% + mean%)
Lower range of stock/index for a T time= current price – current price*(SD% – mean%)
Where, T= time period in days
SD= standard deviation or historical volatility or realized volatility for a T time
mean= average return rate of underlying asset.
But in the normal distribution of any stock/index daily return mean is equal to zero.
So range calculation formula is-
Upper range of stock/index for a T time= current price + current price*SD%
Lower range of stock/index for a T time= current price – current price*SD%
But in a normal distribution three possible ranges available with possibilities of correctness.
So with 68% chance of stock/index range-
Upper range of stock/index for a T time= current price + current price*1*SD%
Lower range of stock/index for a T time= current price – current price*1*SD%
So with 95% chance of stock/index range-
Upper range of stock/index for a T time= current price + current price*2*SD%
Lower range of stock/index for a T time= current price – current price*2*SD%
So with 99.7% chance of stock/index range-
Upper range of stock/index for a T time= current price + current price*3*SD%
Lower range of stock/index for a T time= current price – current price*3*SD%
Why I am calculating range of underlying asset? because of we could understand the current situation of underlying asset price. Meant to say that we are where to from top resistance and bottom support for a last T time frame if range calculated by support and resistance level of underlying price. Then we have to get current price position in the calculated resistance price range or support price range like as near +1sd or -1sd, +2sd or -2sd, +3sd or -3sd. Suppose that current position is near -2sd, then 95% chances to price trend reverse and when -3sd, then 99.7% chances underlying price revert.
When to use resistance price for underlying price range calculation and when to use support price? Suppose that your selected underlying asset price in down trend then you have to know what is the down position from top most resistance price, than you have to take a good decision. Like that you have to know current price position of up trend from calculating range by support price. Suppose that for a up trend from a last support is +0.5SD then chance it vary up to +3SD.
After all calculation we have to ensure that we have to protect our position for a downside if prove wrong, and participate if position cost will be lesser, with predefined profit and loss.
Strategy notes for a bull call spread option strategy:
The bull call spread option strategy comes usable when you have a moderately bullish view on the stock/index. The bull call spread is a two leg option strategy mostly involving ATM and OTM options.
To implement bull call spread-
Leg 1- Buy 1-ATM (LK-lower strike) call option
Leg 2- Sell 1-OTM (HK-higher strike) call option
When take positions ensure that both leg option contracts should be same underlying asset, same expiry date, and with same quantity of options. Also ensure that when you take position in both leg then take position in both leg same time.
Example of bull call spread option strategy:
For a example of bull call spread option strategy, we are taking Nifty options contract.
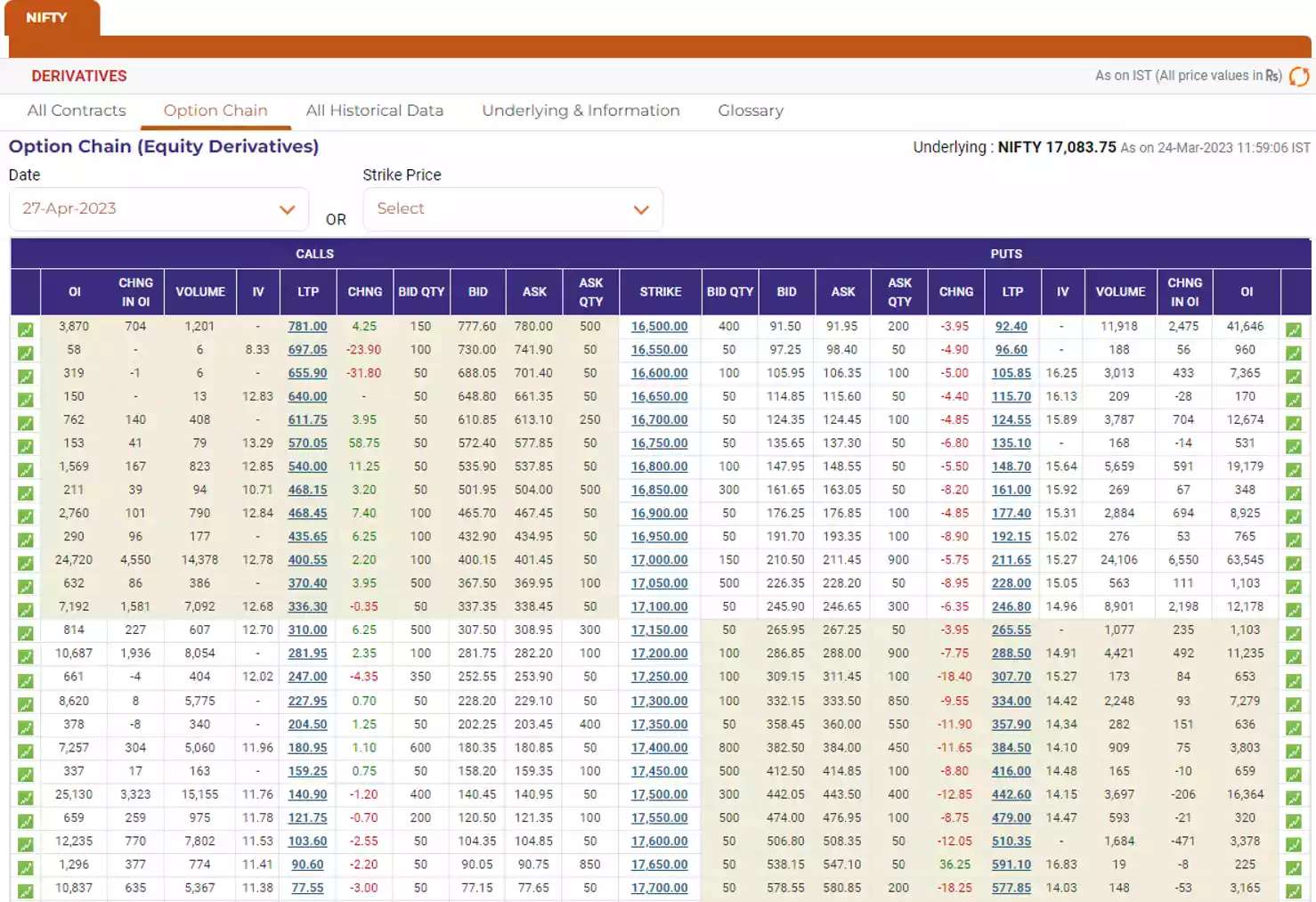
Option contract- Nifty 27Apr … CE
Today’s date- 24/03/2023
Expiry date- 27/04/2023
Underlying asset- Nifty 50
Directional view/outlook- Moderately bullish
Spot price (S)- 17084/-
Spread and strike price selection for a bull call spread option strategy:
As we know that spread is the difference between higher strike price minus lower strike price. For a near strike lower is the spread and for a far strike higher is the spread. So for a lower spread required movement of underlying asset price (spot price) lower and for a higher spread required movement of spot price higher.
So according to your spot price movement or your target price you should select spread. Some strike differences or spread is which mostly used are 100/-, 200/-, 300/-. Also keep in mind for what time period this spread or target price is for.
Mostly used strike combination is ATM+OTM. but also used other strike combination of ITM+OTM, ITM+ATM, and OTM+OTM.
In the table below, we will look at different spreads and different strike combinations to see which one is better.
For spread= 100,
| Generalization | OTM+OTM | ATM+OTM | ITM+OTM | ITM+ATM |
| LK | 17200 | 17100 | 17050 | 17000 |
| HK | 17300 | 17200 | 17150 | 17100 |
| Spread | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| LK-PP | 281.95 | 336.3 | 370.4 | 400.55 |
| HK-PR | 227.95 | 281.95 | 310 | 336.3 |
| Net debit | 54 | 54.35 | 60.4 | 64.25 |
| Max loss | 54 | 54.35 | 60.4 | 64.25 |
| Max profit | 46 | 45.65 | 39.6 | 35.75 |
| Break even point | 17254 | 17154.35 | 17110.4 | 17064.24 |
| Risk/reward ratio | 1.17 | 1.19 | 1.53 | 1.8 |
| Remarks | break even point is very high | looks like moderate | profit is very less | risk reward ratio is very high |
According to above table, best combination is ATM+OTM.
For spread= 200,
| Generalization | OTM+OTM | ATM+OTM | ITM+OTM | ITM+ATM |
| LK | 17200 | 17100 | 17000 | 16900 |
| HK | 17400 | 17300 | 17200 | 17100 |
| Spread | 200 | 200 | 200 | 200 |
| LK-PP | 281.95 | 336.3 | 400.55 | 468.45 |
| HK-PR | 180.95 | 227.95 | 281.95 | 336.3 |
| Net debit | 101 | 108.35 | 118.6 | 132.15 |
| Max loss | 101 | 108.35 | 118.6 | 132.15 |
| Max profit | 99 | 91.65 | 81.4 | 67.85 |
| Break even point | 17301 | 17208.35 | 17118.6 | 17032.15 |
| Risk/reward ratio | 1.02 | 1.18 | 1.46 | 1.95 |
| Remarks | break even point is very high | looks like moderate | profit is very less | risk reward ratio is very high |
According to above table, best combination is ATM+OTM.
For spread= 300,
| Generalization | OTM+OTM | ATM+OTM | ITM+OTM | ITM+ATM |
| LK | 17200 | 17100 | 17000 | 16800 |
| HK | 17500 | 17400 | 17300 | 17100 |
| Spread | 300 | 300 | 300 | 300 |
| LK-PP | 281.95 | 336.3 | 400.55 | 540 |
| HK-PR | 140.90 | 180.95 | 227.95 | 336.3 |
| Net debit | 141.05 | 155.35 | 172.6 | 203.7 |
| Max loss | 141.05 | 155.35 | 172.6 | 203.7 |
| Max profit | 158.95 | 144.65 | 127.4 | 96.3 |
| Break even point | 17341.05 | 17255.35 | 17172.6 | 17003.7 |
| Risk/reward ratio | 0.89 | 1.07 | 1.35 | 2.12 |
| Remarks | break even point is very high | looks like moderate | profit is very less | risk reward ratio is very high |
According to above table, best combination is ATM+OTM.
If we go towards Deep ITM (LK) then the profit will be very less but the chance of making profit will be more. Similarly, if we go towards Deep OTM (HK) then the profit will be more but the chance of making profit will be very less. That is, the options contract strategy will expire worthless.
For call spread option strategy best strike combination is ATM+OTM. Where maximum profit and maximum loss is approximate same and break even point is moderate, that means profit chances is moderate.
The selection of spread depends on the target price. Use higher spread if your target price is higher and use lower spread if your target price is lower. Generally lower spread is used for shorter expiry time and higher spread is used for longer expiry time e.g. Weekly/Half monthly option contract is used for spread up to 100-150, for spread up to 150-250 Half monthly/monthly option contracts are used, and for spreads above 250, monthly to quarterly options contracts are used etc.
Trade setup for a bull call spread:
| Leg | Option type | Moneyness | Position | Quantity | Strike price (K) | Premium (P) | Premium type |
| Leg 1 | CE | ATM (LK) | Buy | 1 | 17100/- | 336.30/- | Premium paid (PP) |
| Leg 2 | CE | OTM (HK) | Sell | 1 | 17300/- | 227.95/- | Premium received (PR) |
| Net premium paid | 108.35 | PP – PR |
Buy ATM call option and sell OTM call option so for this both premium difference in debit. Due to net premium paid or in debit so this strategy also known as debit bull spread.
After taking position in both leg in a same time price can move any direction on expiry so we check for various spot price on expiry to get sense of strategy pay offs.
Scenario 1- Spot price expires at below the lower strike price at (S) 17000/-
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= P&L for leg 1 + P&L for leg 2
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= Qty*(max(S-LK,0) – PP) + Qty*(PR – max(S-HK,0))
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 1*(max(17000-17100,0) – 336.30) + 1*(227.95 – max(17000-17300,0))
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= (max(-100,0) – 336.30) + (227.95 – max(-300,0))
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= (0 -336.30) + (227.95 – 0)
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= -336.30 + 227.95
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= -108.35/-
Scenario 2- Spot price expires at the lower strike price at (S) 17100/-
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= P&L for leg 1 + P&L for leg 2
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= Qty*(max(S-LK,0) – PP) + Qty*(PR – max(S-HK,0))
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 1*(max(17100-17100,0) – 336.30) + 1*(227.95 – max(17100-17300,0))
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= (max(0,0) – 336.30) + (227.95 – max(-200,0))
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= (0 -336.30) + (227.95 – 0)
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= -336.30 + 227.95
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= -108.35/-
Scenario 3- Spot price expires at the higher strike price at (S) 17300/-
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= P&L for leg 1 + P&L for leg 2
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= Qty*(max(S-LK,0) – PP) + Qty*(PR – max(S-HK,0))
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 1*(max(17300-17100,0) – 336.30) + 1*(227.95 – max(17300-17300,0))
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= (max(200,0) – 336.30) + (227.95 – max(0,0))
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= (200 -336.30) + (227.95 – 0)
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= -136.30 + 227.95
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 91.65/-
Scenario 4- Spot price expires at above the higher strike price at (S) 17400/-
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= P&L for leg 1 + P&L for leg 2
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= Qty*(max(S-LK,0) – PP) + Qty*(PR – max(S-HK,0))
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 1*(max(17400-17100,0) – 336.30) + 1*(227.95 – max(17400-17300,0))
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= (max(300,0) – 336.30) + (227.95 – max(100,0))
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= (300 -336.30) + (227.95 – 100)
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= -36.30 + 127.95
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 91.65/-
We have seen that when spot price expires at lower strike or below the lower strike then maximum loss is equal to net premium paid (-108.35/-). And when spot price expires at higher strike or above higher strike then maximum profit is equal to 91.65/-, means this profit is equal to difference between strike prices minus net premium paid.
Strategy generalization for a bull call spread option strategy:
Spread= Difference between the higher strike and lower strike price
Spread= 17300-17100
Spread= 200
Net debit= premium paid for lower strike – premium received for higher strike
Net debit= 336.30 – 227.95
Net debit= 108.35/-
Max profit= spread – net debit
Max profit= 200 – 108.35
Max profit= 91.65/-
Max loss= net debit
Max loss= 108.35/-
Break even point= lower strike + net debit
or Break even point= higher strike – max profit
Break even point= 17100 + 108.35
Break even point= 17208.35/–
Max profit at most strike price= at higher strike
Max profit at most strike price= 17300/-
Max loss at lowest strike price= at lower strike
Max loss at lowest strike price= 17100/-
Strategy pay off (P&L) table for bull call spread option strategy:
Strategy pay off or profit and loss of bull call spread option strategy is combined profit and loss of leg 1 and leg 2 positions for various spot prices on expiry.
Use calculator for calculation of pay off schedule or profit and loss:
Pay of schedule:
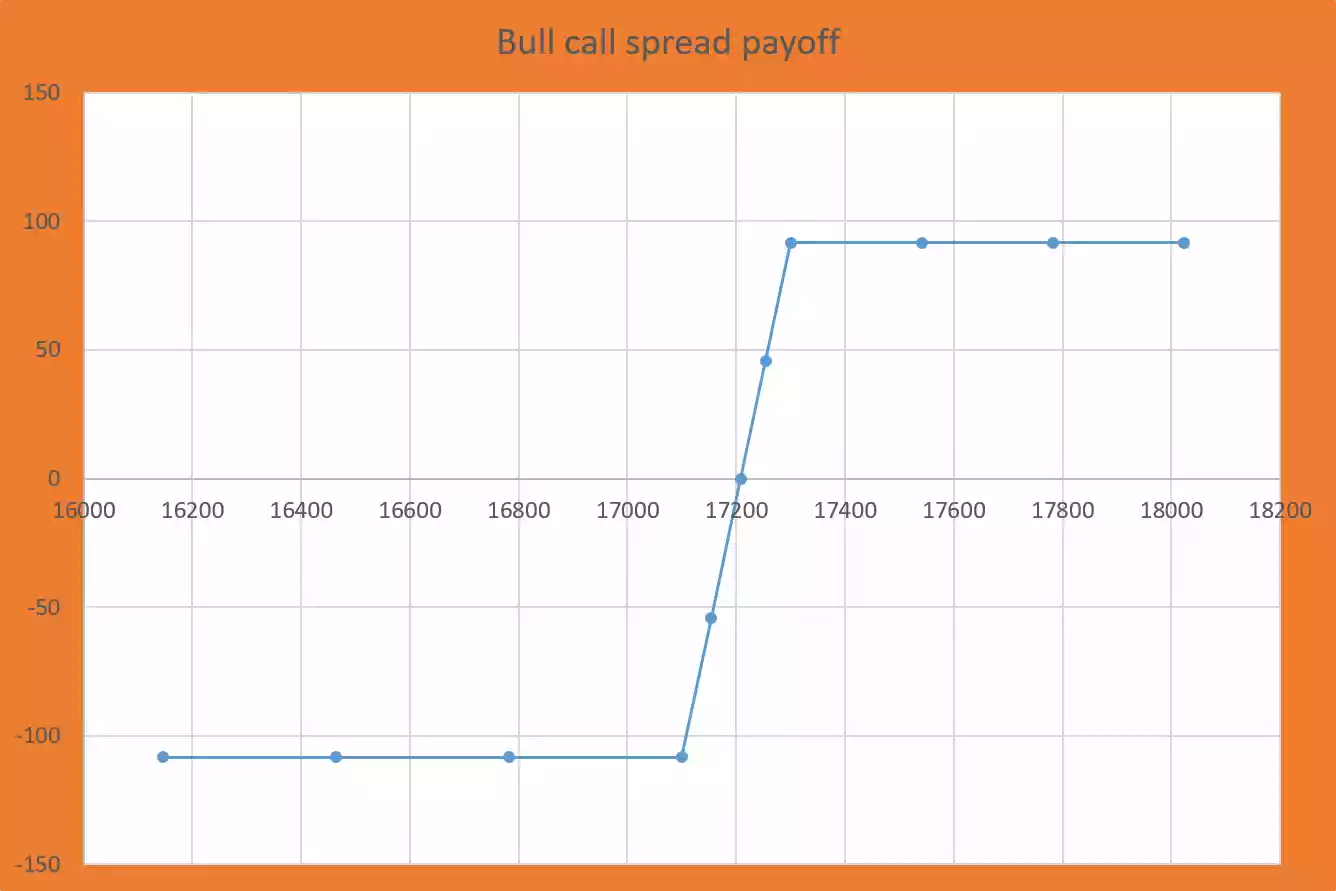
| Various spot prices on expiry (Sf) | Pay off or profit and loss of strategy |
| 16145.46 | -108.35 |
| 16463.64 | -108.35 |
| 16781.82 | -108.35 |
| 17100 | -108.35 |
| 17154.18 | -54.17 |
| 17208.35 | 00 |
| 17254.18 | 45.83 |
| 17300 | 91.65 |
| 17540.85 | 91.65 |
| 17781.70 | 91.65 |
| 18022.55 | 91.65 |
Strategy pay off (P&L) chart for bull call spread option strategy:
Strategy pay off chart is the presentation of profit and loss on y-axis and various spot prices on x-axis.
Why should I use this bull call spread option strategy?
Why I will use this strategy because of I can use long call naked option strategy. Well, the main reason is the reduced strategy cost.
Bull call spread option strategy Greeks:
Below is the option Greeks snapshot, for leg 1 and leg 2 positions-
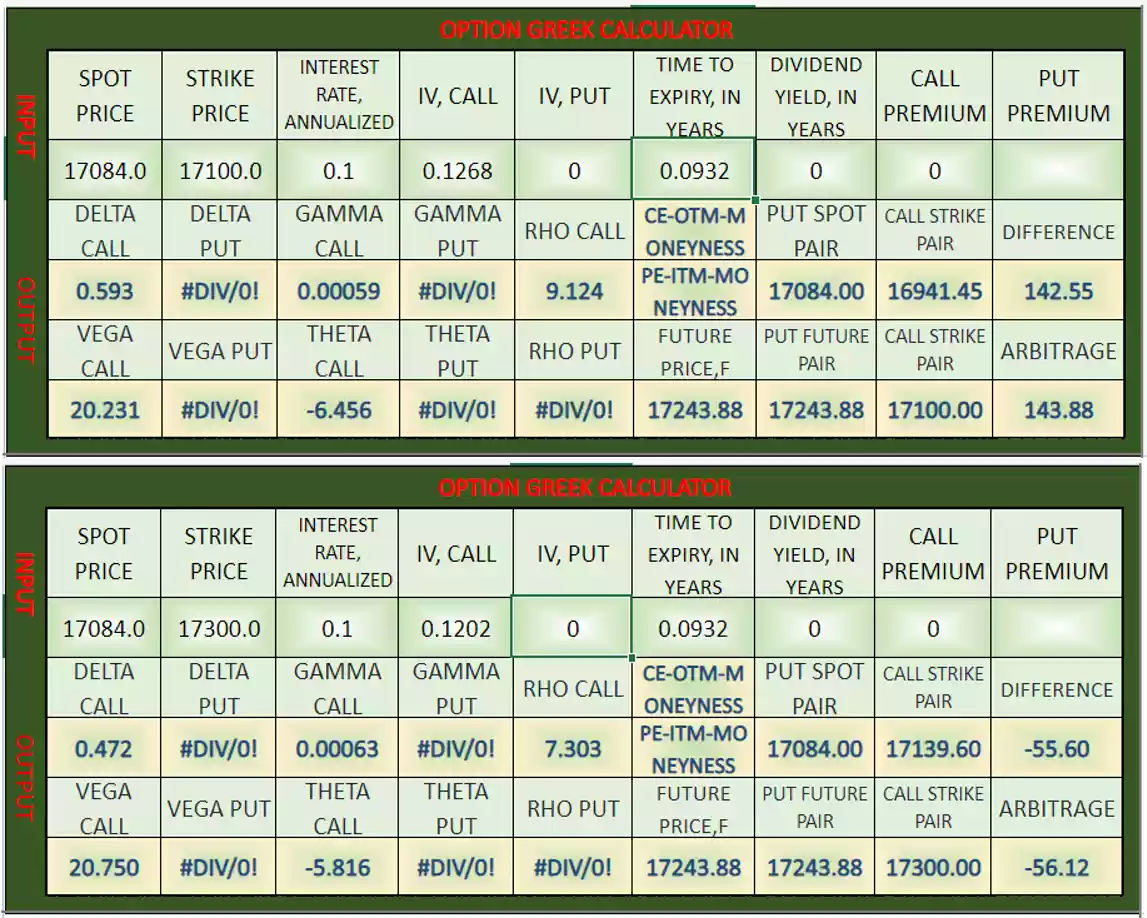
Here are the Greeks associated with a bull call spread:
Delta:
Delta for leg 1 (buy position)= 0.593
Delta for leg 2 (sell position)= 0.472
Associated Delta for bull call spread= -Delta for leg 1 +Delta for leg 2
Negative sign for buy position in leg 1 as a paid and positive sign for sell position in leg 2 as a received.
So Associated Delta= -0.593 + 0.472= -0.121
Associated Delta add with associated premium(net debit or net credit) if spot price increase, and associated Delta minus with associated premium(net debit or net credit) if spot price decrease.
Gamma:
Gamma for leg 1 (buy position)= 0.00059
Gamma for leg 2 (sell position)= 0.00063
Associated Gamma for bull call spread= -Gamma for leg 1 +Gamma for leg 2
Negative sign for buy position in leg 1 as a paid and positive sign for sell position in leg 2 as a received.
So Associated Gamma= -0.00059 +0.00063= 0.00004
Associated Gamma add with associated Delta if spot price increase, and associated Gamma minus with associated Delta if spot price decrease.
Theta:
Theta for leg 1 (buy position)= -6.456
Theta for leg 2 (sell position)= -5.816
Associated Theta for bull call spread= -absolute value of Theta for leg 1 +absolute value of Theta for leg 2
Negative sign for buy position in leg 1 as a paid and positive sign for sell position in leg 2 as a received.
So Associated Theta= -6.456 +5.816= -0.64
Associated Theta add with associated premium(net debit or net credit) if time increase, and associated Theta minus with associated premium(net debit or net credit) if time decrease.
Vega:
Vega for leg 1 (buy position)= 20.231
Vega for leg 2 (sell position)= 20.750
Associated Vega for bull call spread= -Vega for leg 1 + Vega for leg 2
Negative sign for buy position in leg 1 as a paid and positive sign for sell position in leg 2 as a received.
So Associated Vega= -20.231 + 20.750= 0.519
Associated Vega add with associated premium(net debit or net credit) if implied volatility increase, and associated Vega minus with associated premium(net debit or net credit) if implied volatility decrease.
Rho:
Rho for leg 1 (buy position)= 9.124
Rho for leg 2 (sell position)= 7.303
Associated Rho for bull call spread= -Rho for leg 1 + Rho for leg 2
Negative sign for buy position in leg 1 as a paid and positive sign for sell position in leg 2 as a received.
So Associated Rho= -9.124 + 7.303= -1.821
Associated Rho add with associated premium(net debit or net credit) if interest rate increase, and associated Rho minus with associated premium(net debit or net credit) if interest rate decrease.
All associated option Greeks will not be the same during the life of the option, it will change from time to time, and will change with the movement of the spot price and other variables.
Overall, a bull call spread is a limited-risk, limited-reward options strategy that can be used to profit from bullish moves in the underlying asset. But according to Associated Option Greeks, gains and losses don’t happen overnight, it takes time to expire.
Bear call spread option strategy:
Bear call spread option strategy used when your outlook on market moderately bearish not aggressive. Here we will understand the market outlook or directional view of underlying asset price by analysis of underlying asset such analysis as economy analysis, industry/sector analysis, technical analysis, fundamental analysis etc. With these analysis keep in mind current news and events of underlying asset and all market events. For detail reading of market analysis visit above.
Strategy notes for a bear call spread option strategy:
The bear call spread option strategy comes usable when you have a moderately bearish view on the stock/index. The bear call spread is a two leg option strategy mostly involving OTM and OTM options.
To implement bear call spread-
Leg 1- Sell 1-OTM (LK-lower strike) call option
Leg 2- Buy 1-OTM (HK-higher strike) call option
When take positions ensure that both leg option contracts should be same underlying asset, same expiry date, and with same quantity of options. Also ensure that when you take position in both leg then take position in both leg same time.
Example of bear call spread option strategy:
For a example of bear call spread option strategy, we are taking Nifty options contract.

Option contract- Nifty 27Apr … CE
Today’s date- 24/03/2023
Expiry date- 27/04/2023
Underlying asset- Nifty 50
Directional view/outlook- Moderately bearish
Spot price (S)- 17084/-
Spread and strike price selection for a bear call spread option strategy:
In the table below, we will look at different spreads and different strike combinations to see which one is better. The different strike combination is ATM+OTM, ITM+OTM, ITM+ATM, and OTM+OTM. And different spread is 100, 200, 300 etc.
For spread= 100,
| Generalization | OTM+OTM | ATM+OTM | ITM+OTM | ITM+ATM |
| LK | 17200 | 17100 | 17050 | 17000 |
| HK | 17300 | 17200 | 17150 | 17100 |
| Spread | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| LK-PR | 281.95 | 336.3 | 370.4 | 400.55 |
| HK-PP | 227.95 | 281.95 | 310 | 336.3 |
| Net credit | 54 | 54.35 | 60.4 | 64.25 |
| Max profit | 54 | 54.35 | 60.4 | 64.25 |
| Max loss | 46 | 45.65 | 39.6 | 35.75 |
| Break even point | 17254 | 17154.35 | 17110.4 | 17064.24 |
| Risk/reward ratio | 0.85 | 0.84 | 0.66 | 0.56 |
| Remarks | looks like moderate | break even point is very less | break even point is very less | break even point is very less |
According to above table, best combination is OTM+OTM.
For spread= 200,
| Generalization | OTM+OTM | ATM+OTM | ITM+OTM | ITM+ATM |
| LK | 17200 | 17100 | 17000 | 16900 |
| HK | 17400 | 17300 | 17200 | 17100 |
| Spread | 200 | 200 | 200 | 200 |
| LK-PR | 281.95 | 336.3 | 400.55 | 468.45 |
| HK-PP | 180.95 | 227.95 | 281.95 | 336.3 |
| Net credit | 101 | 108.35 | 118.6 | 132.15 |
| Max profit | 101 | 108.35 | 118.6 | 132.15 |
| Max loss | 99 | 91.65 | 81.4 | 67.85 |
| Break even point | 17301 | 17208.35 | 17118.6 | 17032.15 |
| Risk/reward ratio | 0.98 | 0.85 | 0.69 | 0.51 |
| Remarks | looks like moderate | break even point is very less | break even point is very less | break even point is very less |
According to above table, best combination is OTM+OTM.
For spread= 300,
| Generalization | OTM+OTM | ATM+OTM | ITM+OTM | ITM+ATM |
| LK | 17200 | 17100 | 17000 | 16800 |
| HK | 17500 | 17400 | 17300 | 17100 |
| Spread | 300 | 300 | 300 | 300 |
| LK-PR | 281.95 | 336.3 | 400.55 | 540 |
| HK-PP | 140.90 | 180.95 | 227.95 | 336.3 |
| Net credit | 141.05 | 155.35 | 172.6 | 203.7 |
| Max profit | 141.05 | 155.35 | 172.6 | 203.7 |
| Max loss | 158.95 | 144.65 | 127.4 | 96.3 |
| Break even point | 17341.05 | 17255.35 | 17172.6 | 17003.7 |
| Risk/reward ratio | 1.13 | 0.93 | 0.74 | 0.47 |
| Remarks | risk/reward ratio is high but break even point is also high so its combination is best | looks like moderate | break even point is very less | break even point is very less |
As per the above table, the best combination is OTM+OTM but we can also take ATM+OTM as a combination. When we shift to OTM options, the profit potential is higher, but the volume profit is less and the volume loss is higher. Similarly, when we move to ITM options, the probability of loss is higher as the break even point is closer to the spot price, but the quantitative loss is lower.
Trade setup for a bull call spread:
| Leg | Option type | Moneyness | Position | Quantity | Strike price (K) | Premium (P) | Premium type |
| Leg 1 | CE | OTM (LK) | Sell | 1 | 17200/- | 281.95/- | Premium received (PR) |
| Leg 2 | CE | OTM (HK) | Buy | 1 | 17500/- | 140.90/- | Premium paid (PP) |
| Net premium received | 141.05 | PR – PP |
Sell OTM (LK) call option and buy OTM (HK) call option so for this both premium difference in credit. Due to net premium received or in credit so this strategy also known as credit bull spread.
After taking position in both leg in a same time price can move any direction on expiry so we check for various spot price on expiry to get sense of strategy pay offs.
Scenario 1- Spot price expires at below the lower strike price at (S) 17000/-
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= P&L for leg 1 + P&L for leg 2
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= Qty*(PR – max(S-LK,0)) + Qty*(max(S-HK,0) – PP)
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 1*(281.95 – max(17000-17200,0)) + 1*(max(17000-17500,0) – 140.90)
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= (281.95 – max(-200,0)) + (max(-500,0) – 140.90)
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= (281.95 – 0) + (0 – 140.90)
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 281.95 – 140.90
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 141.05/-
Scenario 2- Spot price expires at the lower strike price at (S) 17200/-
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= P&L for leg 1 + P&L for leg 2
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= Qty*(PR – max(S-LK,0)) + Qty*(max(S-HK,0) – PP)
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 1*(281.95 – max(17200-17200,0)) + 1*(max(17200-17500,0) – 140.90)
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= (281.95 – max(0,0)) + (max(-300,0) – 140.90)
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= (281.95 – 0) + (0 – 140.90)
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 281.95 – 140.90
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 141.05/-
Scenario 3- Spot price expires at the higher strike price at (S) 17500/-
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= P&L for leg 1 + P&L for leg 2
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= Qty*(PR – max(S-LK,0)) + Qty*(max(S-HK,0) – PP)
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 1*(281.95 – max(17500-17200,0)) + 1*(max(17500-17500,0) – 140.90)
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= (281.95 – max(300,0)) + (max(0,0) – 140.90)
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= (281.95 – 300) + (0 – 140.90)
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= -18.05 – 140.90
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= -158.95/-
Scenario 4- Spot price expires at above the higher strike price at (S) 17700/-
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= P&L for leg 1 + P&L for leg 2
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= Qty*(PR – max(S-LK,0)) + Qty*(max(S-HK,0) – PP)
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= 1*(281.95 – max(17700-17200,0)) + 1*(max(17700-17500,0) – 140.90)
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= (281.95 – max(500,0)) + (max(200,0) – 140.90)
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= (281.95 – 500) + (200 – 140.90)
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= -218.05 + 59.1
Pay off (P&L) of strategy= -158.95/-
We have seen that when spot price expires at lower strike or below the lower strike then maximum profit is equal to net premium received 141.05/-. And when spot price expires at higher strike or above higher strike then maximum loss is equal to -158.95/-, means this loss is equal to difference between strike prices minus net premium received.
Strategy generalization for a bear call spread option strategy:
Spread= Difference between the higher strike and lower strike price
Spread= 17500-17200
Spread= 300
Net credit= premium received for lower strike – premium paid for higher strike
Net credit= 281.95 – 140.90
Net credit= 141.05/-
Max loss= spread – net credit
Max loss= 300 – 141.05
Max loss= 158.95/-
Max profit= net credit
Max profit= 141.05/-
Break even point= lower strike + net credit
or Break even point= higher strike – max loss
Break even point= 17200 + 141.05
Break even point= 17341.05/–
Max profit at lowest strike price= at lower strike
Max profit at lowest strike price= 17200/-
Max loss at most strike price= at higher strike
Max loss at most strike price= 17500/-
Strategy pay off (P&L) table for bear call spread option strategy:
Strategy pay off or profit and loss of bear call spread option strategy is combined profit and loss of leg 1 and leg 2 positions for various spot prices on expiry.
Use calculator for calculation of pay off schedule or profit and loss:
Pay of schedule:
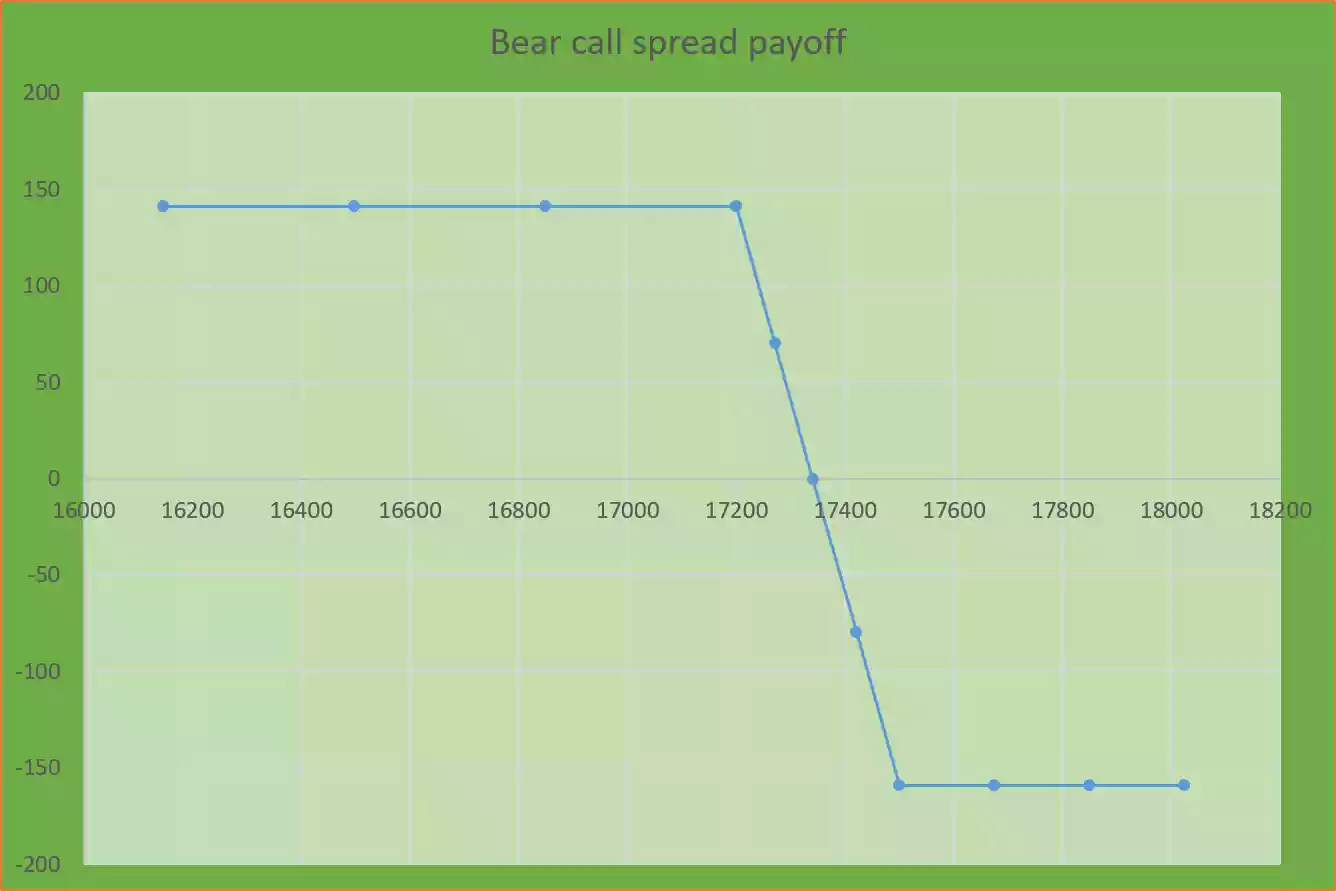
| Various spot prices on expiry (Sf) | Pay off or profit and loss of strategy |
| 16145.46 | 141.05 |
| 16496.98 | 141.05 |
| 16848.49 | 141.05 |
| 17200 | 141.05 |
| 17270.53 | 70.52 |
| 17341.05 | 00 |
| 17420.53 | -79.48 |
| 17500 | -158.95 |
| 17674.18 | -158.95 |
| 17848.36 | -158.95 |
| 18022.54 | -158.95 |
Strategy pay off (P&L) chart for bear call spread option strategy:
Strategy pay off chart is the presentation of profit and loss on y-axis and various spot prices on x-axis.
Why should I use this bear call spread option strategy?
Why I will use this strategy because of I can use short call naked option strategy. Well, the main reason is the protect unlimited loss.
Bear call spread option strategy Greeks:
Below is the option Greeks snapshot, for leg 1 and leg 2 positions-
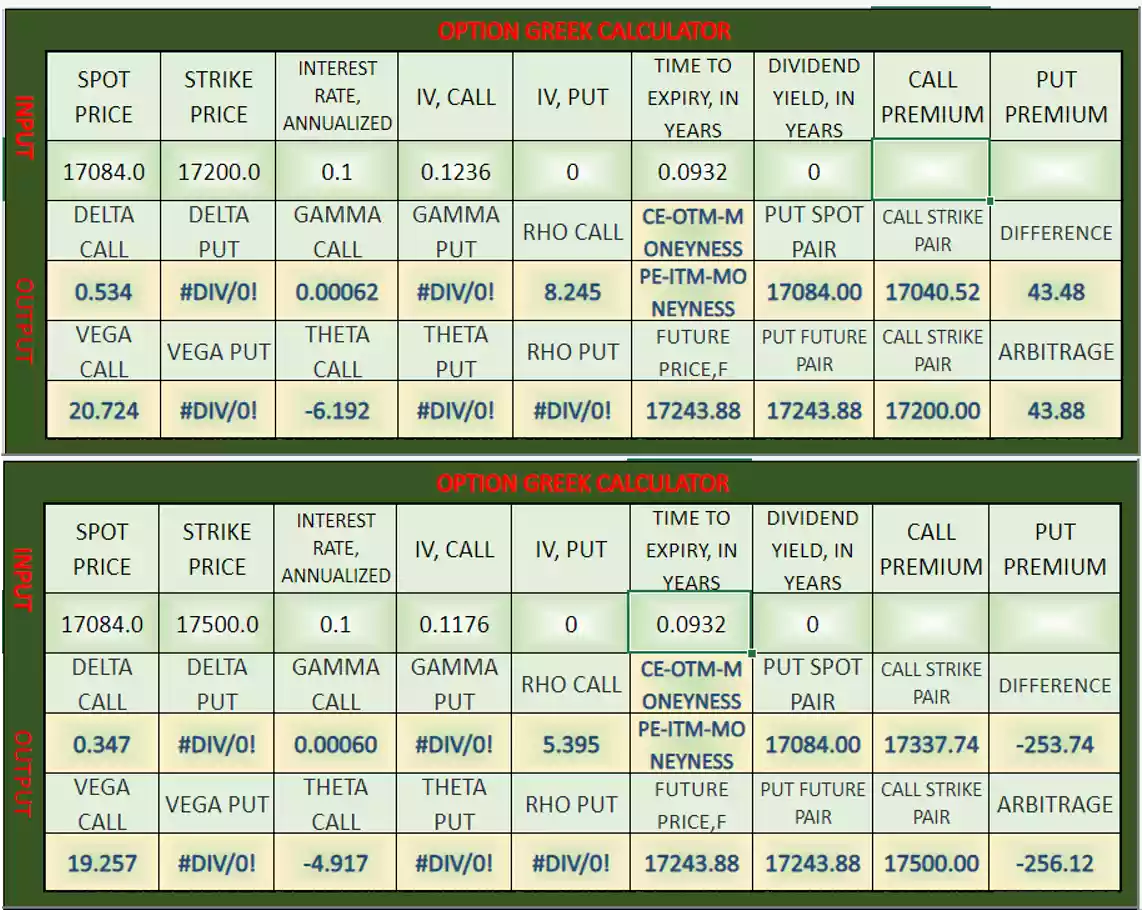
Here are the Greeks associated with a bear call spread:
Delta:
Delta for leg 1 (sell position)= 0.534
Delta for leg 2 (buy position)= 0.347
Associated Delta for bear call spread= Delta for leg 1 – Delta for leg 2
Negative sign for buy position in leg 2 as a paid and positive sign for sell position in leg 1 as a received.
So Associated Delta= +0.534 – 0.347= 0.187
Associated Delta add with associated premium(net debit or net credit) if spot price increase, and associated Delta minus with associated premium(net debit or net credit) if spot price decrease.
Gamma:
Gamma for leg 1 (sell position)= 0.00062
Gamma for leg 2 ( (buy position)= 0.00060
Associated Gamma for bear call spread= Gamma for leg 1 – Gamma for leg 2
Negative sign for buy position in leg 2 as a paid and positive sign for sell position in leg 1 as a received.
So Associated Gamma= 0.00062 – 0.00060= 0.00002
Associated Gamma add with associated Delta if spot price increase, and associated Gamma minus with associated Delta if spot price decrease.
Theta:
Theta for leg 1 (sell position)= -6.192
Theta for leg 2 (buy position)= -4.917
Associated Theta for bear call spread= + absolute value of Theta for leg 1 – absolute value of Theta for leg 2
Negative sign for buy position in leg 2 as a paid and positive sign for sell position in leg 1 as a received.
So Associated Theta= 6.192 – 4.917= 1.275
Associated Theta add with associated premium(net debit or net credit) if time increase, and associated Theta minus with associated premium(net debit or net credit) if time decrease.
Vega:
Vega for leg 1 (sell position)= 20.231
Vega for leg 2 (buy position)= 20.750
Associated Vega for bear call spread= Vega for leg 1 – Vega for leg 2
Negative sign for buy position in leg 2 as a paid and positive sign for sell position in leg 1 as a received.
So Associated Vega= 20.724 – 19.257= 1.467
Associated Vega add with associated premium(net debit or net credit) if implied volatility increase, and associated Vega minus with associated premium(net debit or net credit) if implied volatility decrease.
Rho:
Rho for leg 1 (sell position)= 8.245
Rho for leg 2 (buy position)= 5.395
Associated Rho for bear call spread= Rho for leg 1 – Rho for leg 2
Negative sign for buy position in leg 2 as a paid and positive sign for sell position in leg 1 as a received.
So Associated Rho= 8.245 – 5.395= 2.85
Associated Rho add with associated premium(net debit or net credit) if interest rate increase, and associated Rho minus with associated premium(net debit or net credit) if interest rate decrease.
All associated option Greeks will not be the same during the life of the option, it will change from time to time, and will change with the movement of the spot price and the other variables.
Overall, a bear call spread is a limited-risk, limited-reward options strategy that can be used to profit from bearish moves in the underlying asset. But according to Associated Option Greeks, gains and losses don’t happen overnight, it takes time to expire.
